Necroptosis restricts influenza A virus as a stand-alone cell death mechanism
- PMID: 32797196
- PMCID: PMC7596817
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191259
Necroptosis restricts influenza A virus as a stand-alone cell death mechanism
Abstract
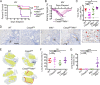
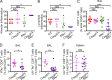
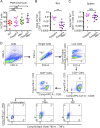
Influenza A virus (IAV) activates ZBP1-initiated RIPK3-dependent parallel pathways of necroptosis and apoptosis in infected cells. Although mice deficient in both pathways fail to control IAV and succumb to lethal respiratory infection, RIPK3-mediated apoptosis by itself can limit IAV, without need for necroptosis. However, whether necroptosis, conventionally considered a fail-safe cell death mechanism to apoptosis, can restrict IAV-or indeed any virus-in the absence of apoptosis is not known. Here, we use mice selectively deficient in IAV-activated apoptosis to show that necroptosis drives robust antiviral immune responses and promotes effective virus clearance from infected lungs when apoptosis is absent. We also demonstrate that apoptosis and necroptosis are mutually exclusive fates in IAV-infected cells. Thus, necroptosis is an independent, "stand-alone" cell death mechanism that fully compensates for the absence of apoptosis in antiviral host defense.
© 2020 Shubina et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: P.G. Thomas reported other from Cytoagents outside the submitted work; in addition, P.G. Thomas had a patent to US201462068561P pending. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
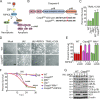
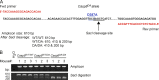
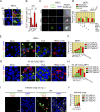
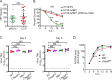
References
-
- Daniels B.P., Kofman S.B., Smith J.R., Norris G.T., Snyder A.G., Kolb J.P., Gao X., Locasale J.W., Martinez J., Gale M. Jr., et al. 2019. The nucleotide sensor ZBP1 and kinase RIPK3 induce the enzyme IRG1 to promote an antiviral metabolic state in neurons. Immunity. 50:64–76.e4. 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.11.017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

