Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 32798468
- PMCID: PMC7426089
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30328-3
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Patients with COVID-19 who develop severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can have symptoms that rapidly evolve to profound hypoxaemia and death. The efficacy of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for patients with severe ARDS in the context of COVID-19 is unclear. We aimed to establish the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with respiratory failure and COVID-19 treated with ECMO.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was done in the Paris-Sorbonne University Hospital Network, comprising five intensive care units (ICUs) and included patients who received ECMO for COVID-19 associated ARDS. Patient demographics and daily pre-ECMO and on-ECMO data and outcomes were collected. Possible outcomes over time were categorised into four different states (states 1-4): on ECMO, in the ICU and weaned off ECMO, alive and out of ICU, or death. Daily probabilities of occupation in each state and of transitions between these states until day 90 post-ECMO onset were estimated with use of a multi-state Cox model stratified for each possible transition. Follow-up was right-censored on July 10, 2020.
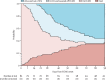
Findings: From March 8 to May 2, 2020, 492 patients with COVID-19 were treated in our ICUs. Complete day-60 follow-up was available for 83 patients (median age 49 [IQR 41-56] years and 61 [73%] men) who received ECMO. Pre-ECMO, 78 (94%) patients had been prone-positioned; their median driving pressure was 18 (IQR 16-21) cm H2O and PaO2/FiO2 was 60 (54-68) mm Hg. At 60 days post-ECMO initiation, the estimated probabilities of occupation in each state were 6% (95% CI 3-14) for state 1, 18% (11-28) for state 2, 45% (35-56) for state 3, and 31% (22-42) for state 4. 35 (42%) patients had major bleeding and four (5%) had a haemorrhagic stroke. 30 patients died.
Interpretation: The estimated 60-day survival of ECMO-rescued patients with COVID-19 was similar to that of studies published in the past 2 years on ECMO for severe ARDS. If another COVID-19 outbreak occurs, ECMO should be considered for patients developing refractory respiratory failure despite optimised care.
Funding: None.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
ECMO for severe ARDS associated with COVID-19: now we know we can, but should we?Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Nov;8(11):1066-1068. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30357-X. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32798470 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Overcoming bleeding events related to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in COVID-19 - Authors' reply.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Dec;8(12):e89. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30468-9. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33129419 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Overcoming bleeding events related to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in COVID-19.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Dec;8(12):e87-e88. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30467-7. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33129422 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Combes A, Hajage D, Capellier G. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1965–1975. - PubMed
-
- Goligher EC, Tomlinson G, Hajage D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and posterior probability of mortality benefit in a post hoc Bayesian analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320:2251–2259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

