Performance of the BD FACSPresto near to patient analyzer in comparison with representative conventional CD4 instruments in Cameroon
- PMID: 32799909
- PMCID: PMC7429678
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-020-00309-9
Performance of the BD FACSPresto near to patient analyzer in comparison with representative conventional CD4 instruments in Cameroon
Abstract
Background: In the context of scaling the viral load in resource limited settings, following HIV infected patient's adults and children with CD4+ T-lymphocyte count still very important in settings where the decentralization of treatment still has some challenges. Effective HIV monitoring in these resource-constrained settings needs affordable and reliable CD4+ T lymphocytes enumeration methods. We investigated the validity of a BD FACSPresto POC which is a dedicated system for enumeration that uses immunofluorescent technologies. In this study, we have assessed the sensitivity, specificity and correlation between most representative flow cytometry instruments present in Cameroon with more than 5000 CD4 T cells tests per year including FACSCalibur, FACSCount, and PIMA POC from Becton-Dickinson and ALERE respectively.
Methods: 268 patients aged from 1 to 72 years old were enrolled and included in the study after inform consent. The BD FACSPresto POC CD4+ T cell technology was placed at CIRCB and operated by technician staff. HIV infected patients were from Chantal BIYA international reference Center (CIRCB), Centre de Sante Catholique de NKOLODOM, Centre de Sante Catholique de BIKOP and CASS de Nkolndongo-Yaounde We compared the accuracy of the BD FACSPresto and three existing reference technologies with more than 5000 tests per year like FACSCalibur, FACSCount and PIMA according to the number of CD4 test done per year and their repartition in the country. Bland-Altman method and correlation analysis were used to estimate mean bias and 95% limits of agreement and to compare the methods, including analysis by subgroup of participant gestational age. In addition sensitivity and specificity were determined. Statistical significance was set at P-value < 0.05.
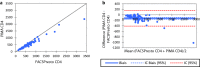
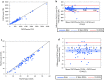
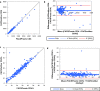
Results: The BD FACSPresto POC system has excellent precision, accuracy and linearity for CD4+ T lymphocytes enumeration. Good correlations were obtained between the BD FACSPresto poc system and other single platform methods. Bland-Altman plots showed interchangeability between two machines mean bias BD-FACSPresto vs PIMA = - 126,522(- 161,221 to - 91,822) BD-FACSPresto vs FACSCount = - 38,708 (- 58,935 to - 18,482) and FACSPresto vs FACSCALIBUR = 0.791(- 11,908 to 13,491). Mean difference with Absolute CD4+ T-lymphocyte values obtained from the BD FACSPresto system correlated well with PIMA, FACSCount, and FACSCalibur method with R2 equal to 0.88, 0.92 and 0.968 respectively with P < 0.001 for all. The mean comparison between values obtained from BD FACSPresto with PIMA, FACSCount, and FACSCalibur using paired T test give P = 0.17, P = 0.5 and P = 0.6 respectively meaning that there is no significant differences between values obtained with BD FACSPresto and PIMA, FACSCount or FACSCalibur CD4 enumeration machines. Further analysis revealed close agreement between all the three instruments with no significant difference between the forth methods (P = 0.91).
Conclusion: This BD-FACSPresto POC system is a simple, robust and reliable system for enumeration of absolute and percentage of CD4+ T-lymphocytes especially suitable for remote areas with limited resources. Having one BD-FACSPresto POC system easy to use, should reduce the cost and thus increase and improved access to CD4 testing for HIV infected patients in resource-constrained countries. BD-FACSPresto POC CD4 will enable reduction in patient time and improve the overall quality of ART service count and may improve test access in remote areas. This technology can allow for greater decentralization and wider access to CD4 testing and ART.
Keywords: BD FACSPresto; CD4 T lymphocyte; FACSCalibur; FACSCount; HIV; PIMA POC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance evaluation of BD FACSPresto™ point of care CD4 analyzer to enumerate CD4 counts for monitoring HIV infected individuals in Nigeria.PLoS One. 2017 May 25;12(5):e0178037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178037. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542359 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of two POC technologies for CD4 count in Morocco.AIDS Res Ther. 2020 Jun 10;17(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12981-020-00289-w. AIDS Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32522235 Free PMC article.
-
The BD FACSPresto Point of Care CD4 Test Accurately Enumerates CD4+ T Cell Counts.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 31;10(12):e0145586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145586. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26720601 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a flow cytometry method for CD4 T cell enumeration based on volumetric primary CD4 gating using thermoresistant reagents.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Sep 30;372(1-2):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21835181 Review.
-
Absolute and percent CD4+ T-cell enumeration by flow cytometry using capillary blood.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Sep 30;372(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 20. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21787779 Review.
Cited by
-
Accurate and reproducible enumeration of CD4 T cell counts and Hemoglobin levels using a point of care system: Comparison with conventional laboratory based testing systems in a clinical reference laboratory in Cameroon.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 20;19(3):e0297790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297790. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38507344 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of POC CD4 Detecting Mode in District or County Labs - Jiangsu Province, China, 2021.China CDC Wkly. 2022 Nov 25;4(47):1059-1065. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2022.213. China CDC Wkly. 2022. PMID: 36751439 Free PMC article.
-
The Diagnostic Performance of the Visitect Advanced Disease Point-Of-Care CD4 Platform: A Pragmatic, Mixed-Methods, Multisite Validation, Costing, and Qualitative Analysis.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024 Dec 1;97(4):387-396. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003505. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39159398 Clinical Trial.
-
Peripheral blood lymphocyte immunophenotyping (TBNK) - a comparison of BD FACSCanto II and BD FACSLyric flow cytometry analysers.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024;49(1):45-51. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2024.135939. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38812607 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a collaborative model for successful implementation of a National CD4 enumeration EQA program in Cameroon.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 2;11(1):11536. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91015-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34078982 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

