When health services are powerless to prevent suicide: results from a linkage study of suicide among men with no service contact in the year prior to death
- PMID: 32799985
- PMCID: PMC8060821
- DOI: 10.1017/S1463423619000057
When health services are powerless to prevent suicide: results from a linkage study of suicide among men with no service contact in the year prior to death
Abstract
Aims: To investigate cases of suicide in which there was no healthcare contact, by looking at history of help-seeking and evidence of previous mental health vulnerability. To identify any life events associated with suicide for which individuals did not seek help.
Background: Previous research has suggested that non-consultation is the main barrier to suicide prevention among men. Estimates suggest approximately 22% of men who die by suicide have not consulted their GP in the year before their death. Little is known about the lifetime pattern of engagement with services among these individuals and whether or not this may influence their help-seeking behaviour before death.
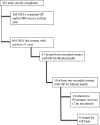
Methods: Coroner records of suicide deaths in Northern Ireland over 2 years were linked to general practice (GP) records. This identified 63 individuals who had not attended health services in the 12 months before death. Coroner's data were used to categorise life events associated with the male deaths. Lifetime mental health help-seeking at the GP was assessed.
Findings: The vast majority of individuals who did not seek help were males (n=60, 15% of all suicide deaths). Lack of consultation in the year before suicide was consistent with behaviour over the lifespan; over two-thirds had no previous consultations for mental health. In Coroner's records, suicides with no prior consultation were primarily linked to relationship breakdown and job loss. These findings highlight the limitations of primary care in suicide prevention as most had never attended GP for mental health issues and there was a high rate of supported consultation among those who had previously sought help. Public health campaigns that promote service use among vulnerable groups at times of crisis might usefully be targeted at those likely to be experiencing financial and relationship issues.
Keywords: general practice; help-seeking; mental health; men’s health; suicide.
Figures
References
-
- Authors (2016.
-
- British Medical Association (2016) Health in all policies: health, austerity and welfare reform. London: BMA House.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical