A comprehensive review on traditional uses, chemical compositions, pharmacology properties and toxicology of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum
- PMID: 32800929
- PMCID: PMC7422820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113247
A comprehensive review on traditional uses, chemical compositions, pharmacology properties and toxicology of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg (T.hemsleyanum), a rare herbal plant distributed in subtropical areas of mainland China, has become a focus of scientific attention in recent years because of its high traditional value, including uses for treatment of children with fever, pneumonia, asthma, rheumatism, hepatitis, menstrual disorders, scrofula, and pharynx pain.
Aim: This systematic review aims to provide an insightful understanding of traditional uses, chemical composition, pharmacological effect and clinical application of T. hemsleyanum, and lay a foundation for the further study and for the utilization of T. hemsleyanum resource.
Materials and methods: A domestic and overseas literature search in known databases was conducted for published articles using the relevant keywords.
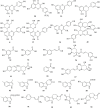
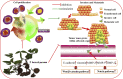
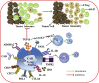
Results: One hundred and forty-two chemical constituents identified from T. hemsleyanum have been reported, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, polysaccharide, organic acids, fatty acids, terpenoids, steroids, amino acid and others. Among these components, flavonoids and polysaccharides were the representative active ingredients of T. hemsleyanum, which have been widely investigated. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that these components exhibited various pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antivirus, antitumor, antipyretic, anti-hepatic injury, immunomodulatory, antibacterial etc. Moreover, different toxicological studies indicated that the clinical dosage of T. hemsleyanum was safe and reliable.
Conclusions: Modern pharmacological studies have well supported and clarified some traditional uses, and T. hemsleyanum has a good prospect for the development of new drugs due to these outstanding properties. However, the present findings did not provide an in-depth evaluation of bioactivity of the extracts, the composition of its active extracts was not clear. Moreover, they were insufficient to satisfactorily explain some mechanisms of action. Data regarding many aspects of T. hemsleyanum, such as links between the traditional uses and bioactivities, pharmacokinetics, quality control standard and the clinical value of active compositions is still limited which need more attention.
Keywords: Chemical composition; Pharmacological activity; Tetrastigma hemsleyanum; Toxicology; Traditional uses.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest pertaining to this manuscript.
Figures





References
-
- Chen H., Liao S.B., Chen D., Xie P., Huang J. Study on the acute toxicity of the anti-inflammatory extract from the aerial part of Tetrastigma Hemsleyanum. J. Fujian Med. Uni. 2017;51:287–290.
-
- Chen L.Y. Study on the chemical constituent and the antitumor activity of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. Fujian Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014:9–14. Fujian.
-
- Chen L.Y., Guo S.H. Progress in studies of chemical composition and pharmacological effects of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. J. Zhejiang Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012;36:1368–1370.
-
- Chen P.R., Li X. Effects of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum on cell factors and immune function of broilers. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2015;44:134–137.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

