Enzymatically synthesized glycogen prevents ultraviolet B-induced cell damage in normal human epidermal keratinocytes
- PMID: 32801467
- PMCID: PMC7417806
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.20-44
Enzymatically synthesized glycogen prevents ultraviolet B-induced cell damage in normal human epidermal keratinocytes
Abstract
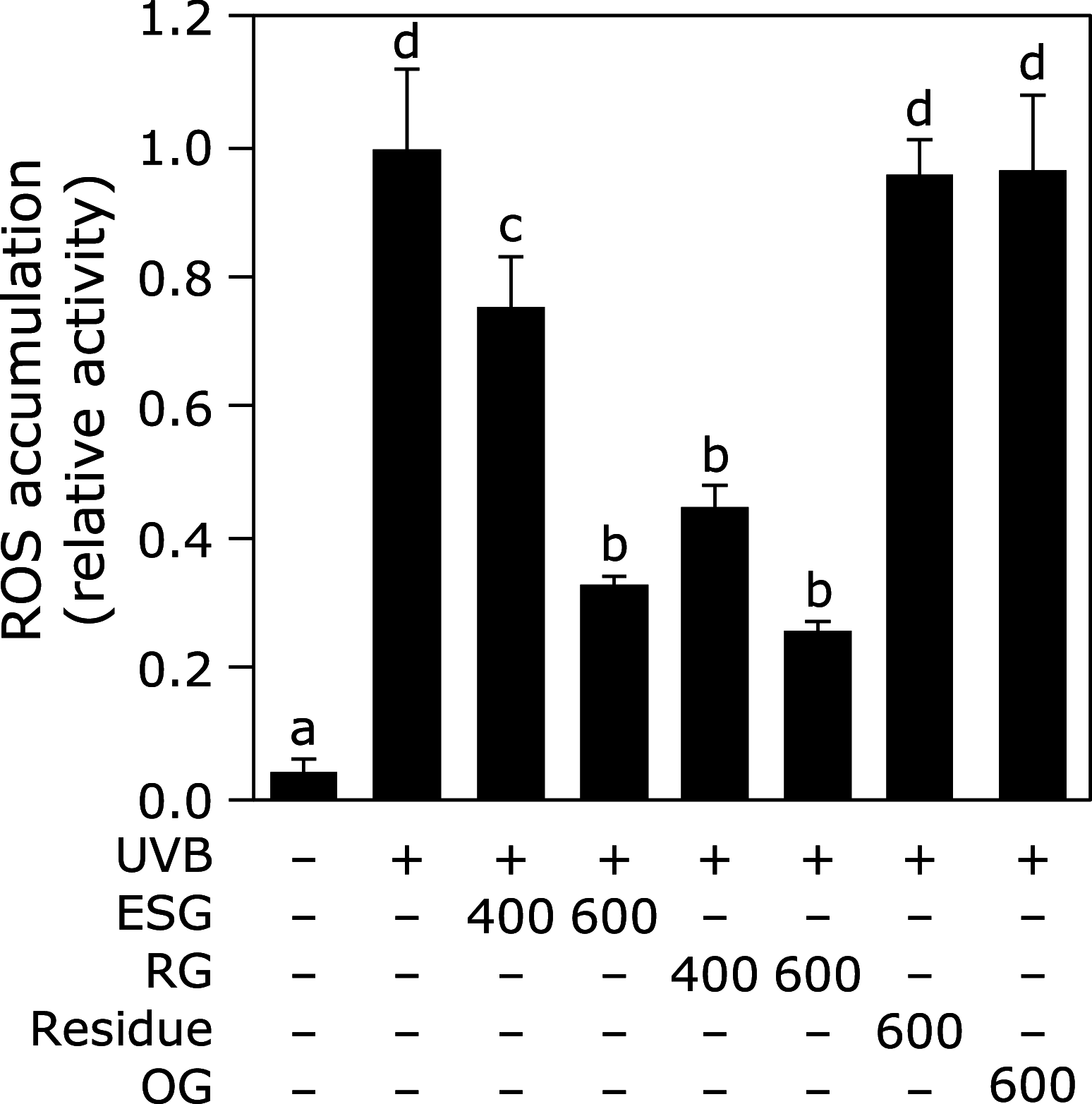
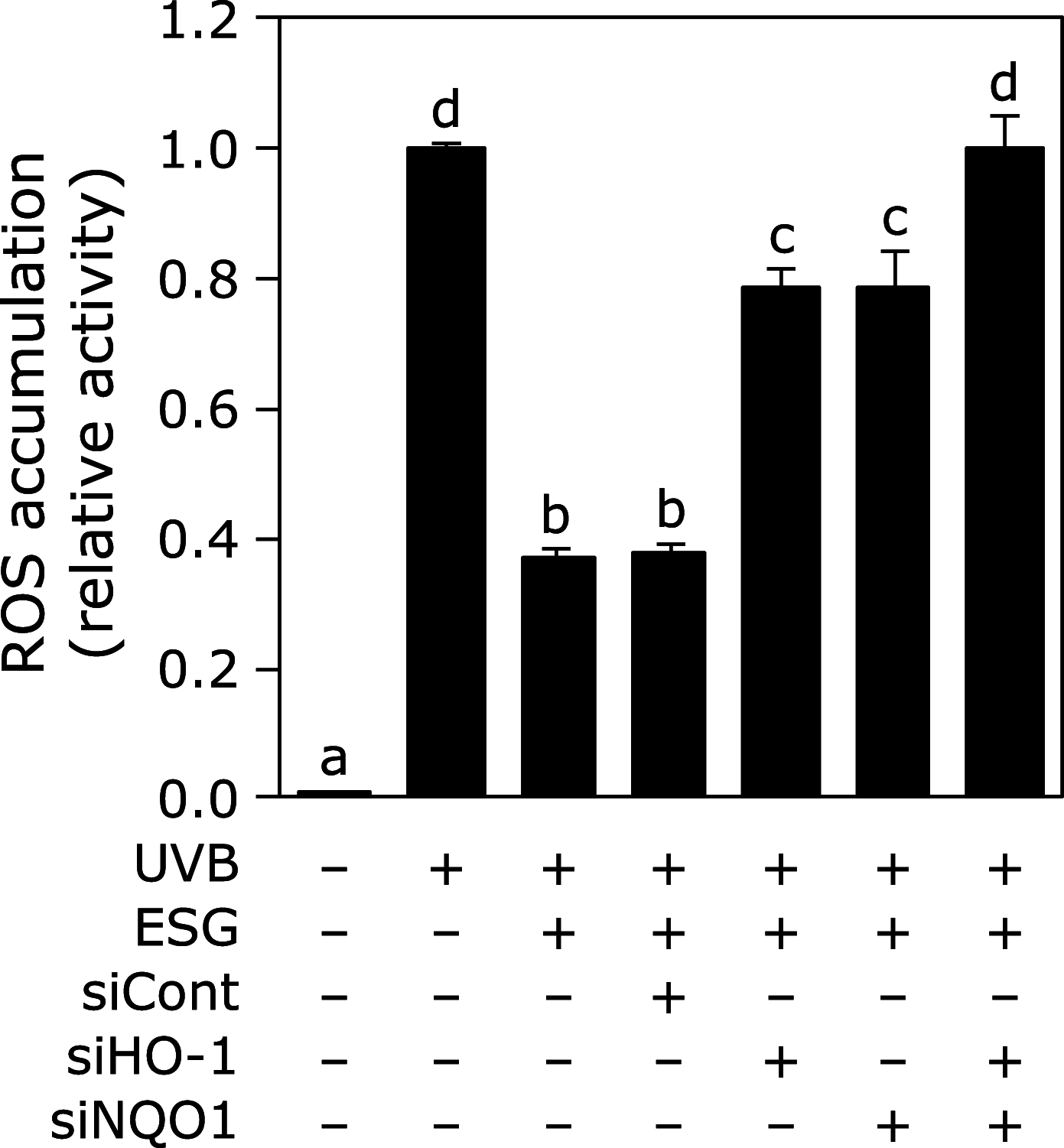
Enzymatically synthesized glycogen is a product from starch. Enzymatically synthesized glycogen has been reported to possess various health beneficial effects such as anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. In this study, we investigated the effect of enzymatically synthesized glycogen on ultraviolet B-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Treatment with enzymatically synthesized glycogen suppressed ultraviolet B-induced reactive oxygen species, caspase-3 activity, and DNA fragmentation in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Furthermore, enzymatically synthesized glycogen increased in the expression level of heme oxygenase-1, NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1, and NF-E2-related factor 2, a transcriptional factor for heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1. Although enzymatically synthesized glycogen did not increase in its mRNA expression level of NF-E2-related factor 2, enzymatically synthesized glycogen retained its protein degradation. Knockdown of heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 canceled enzymatically synthesized glycogen-suppressed reactive oxygen species accumulation in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. It is, therefore, concluded that enzymatically synthesized glycogen inhibited ultraviolet B-induced oxidative stress through increasing the expression level of heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 through the NF-E2-related factor 2 pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes.
Keywords: anti-oxidative protein; enzymatically synthesized glycogen; normal human epidermal keratinocytes; reactive oxygen species; ultraviolet B.
Copyright © 2020 JCBN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare in this study. TF belongs to Ezaki Glico Co. Ltd., and is also a member of Innovative Bioproduction Kobe.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enzymatically synthesized glycogen protects inflammation induced by urban particulate matter in normal human epidermal keratinocytes.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020 Jul;67(1):29-35. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-43. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32801466 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin enhances mitochondrial ATP synthesis, reduces reactive oxygen species formation, and mediates translocation of the nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 resulting in activation of phase-2 antioxidant enzymes (γ-GCS, HO-1, NQO1) in ultraviolet radiation-treated normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK).J Pineal Res. 2016 Sep;61(2):187-97. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12338. Epub 2016 May 21. J Pineal Res. 2016. PMID: 27117941
-
Enzymatically synthesized glycogen inhibits colitis through decreasing oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 May;106:355-367. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.02.048. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28257879
-
Z-ligustilide ameliorated ultraviolet B-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production in human keratinocytes through upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and suppression of NF-κB pathway.Exp Dermatol. 2015 Sep;24(9):703-8. doi: 10.1111/exd.12758. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25977183
-
Antioxidant tert-butylhydroquinone ameliorates arsenic-induced intracellular damages and apoptosis through induction of Nrf2-dependent antioxidant responses as well as stabilization of anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 in human keratinocytes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 May;94:74-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 26878773
Cited by
-
Accumulation of Glycogen and Upregulation of LEA-1 in C. elegans daf-2(e1370) Support Stress Resistance, Not Longevity.Cells. 2022 Jan 12;11(2):245. doi: 10.3390/cells11020245. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053361 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Glycogen on Ceramide Production in Cultured Human Keratinocytes via Acid Sphingomyelinase Activation.J Appl Glycosci (1999). 2021 Jun 11;68(2):41-46. doi: 10.5458/jag.jag.JAG-2020_0012. eCollection 2021. J Appl Glycosci (1999). 2021. PMID: 34429698 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatically synthesized glycogen protects inflammation induced by urban particulate matter in normal human epidermal keratinocytes.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020 Jul;67(1):29-35. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-43. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32801466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verschooten L, Claerhout S, Van Laethem A, Agostinis P, Garmyn M. New strategies of photoprotection. Photochem Photobiol 2006; 82: 1016–1023. - PubMed
-
- Ishii T, Itoh K, Takahashi S, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 16023–16029. - PubMed
-
- Rivas JM, Ullrich SE. Systemic suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by supernatants from UV-irradiated keratinocytes. An essential role for keratinocyte-derived IL-10. J Immunol 1992; 149: 3865–3871. - PubMed
-
- Rivas JM, Ullrich SE. The role of IL-4, IL-10, and TNF-α in the immune suppression induced by ultraviolet radiation. J Leukoc Biol 1994; 56: 769–775. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

