The cacao procyanidin extract-caused anti-hyperglycemic effect was changed by the administration timings
- PMID: 32801470
- PMCID: PMC7417804
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.20-45
The cacao procyanidin extract-caused anti-hyperglycemic effect was changed by the administration timings
Abstract
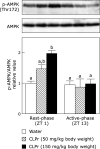
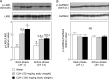
Mammals have the biological clocks with approximately 24 h-rhythm. Energy metabolism including glucose metabolism is regulated by the biological clocks. Glucose metabolism is affected by not only meal volume and its energy but also meal timing. We have reported that cacao liquor procyanidin-rich extract (CLPr) ameliorated the postprandial hyperglycemia through AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. However, the effect of administration timing of CLPr on the postprandial hyperglycemia and its signaling pathway are still unclear. In the present study, we compared the effect of CLPr-administration at the rest-phase (light-period) and active-phase (dark-period) on glucose metabolism. Single oral administration of CLPr to ICR mice at the rest-phase, but not at the active-phase, promoted phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase and its upstream liver kinase B1 and translocation of glucose transporter 4 to the plasma membrane in the skeletal muscle, resulting in reduced postprandial hyperglycemia. These results indicated that the intake of CLPr at the rest-phase more effectively suppressed postprandial hyperglycemia.
Keywords: cacao liquor procyanidin rich extract; circadian rhythm; hyperglycemia; muscle; timing.
Copyright © 2020 JCBN.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cacao liquor procyanidins prevent postprandial hyperglycaemia by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 activity and AMP-activated protein kinase in mice.J Nutr Sci. 2019 Jan 16;8:e2. doi: 10.1017/jns.2018.28. eCollection 2019. J Nutr Sci. 2019. PMID: 30719284 Free PMC article.
-
Cacao liquor procyanidin extract improves glucose tolerance by enhancing GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle.J Nutr Sci. 2012 May 31;1:e2. doi: 10.1017/jns.2012.2. eCollection 2012. J Nutr Sci. 2012. PMID: 25191549 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention mechanisms of glucose intolerance and obesity by cacao liquor procyanidin extract in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6 mice.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Nov 15;527(2):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.018. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22465028
-
Role of High Energy Breakfast "Big Breakfast Diet" in Clock Gene Regulation of Postprandial Hyperglycemia and Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2021 May 5;13(5):1558. doi: 10.3390/nu13051558. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34063109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian desynchrony and glucose metabolism.J Pineal Res. 2024 May;76(4):e12956. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12956. J Pineal Res. 2024. PMID: 38695262 Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian rhythms affect bone reconstruction by regulating bone energy metabolism.J Transl Med. 2021 Sep 27;19(1):410. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03068-x. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34579752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronometabolism: The Timing of the Consumption of Meals Has a Greater Influence Than Glycemic Index (GI) on the Postprandial Metabolome.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 29;13(4):490. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040490. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110149 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Chrononutrition in the Antihypertensive Effects of Natural Bioactive Compounds.Nutrients. 2022 May 4;14(9):1920. doi: 10.3390/nu14091920. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35565887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute and Long Term Effects of a Nutraceutical Combination on Lipid Profile, Glucose Metabolism and Vascular Function in Patients with Dyslipidaemia with and Without Cigarette Smoking.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 Sep;28(5):483-491. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00468-4. Epub 2021 Sep 13. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 34519016 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouting facilitates the antiglycative effect of black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) by promoting the accumulation of isoflavones.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Aug 23;9:100827. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100827. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39281341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reinke H, Asher G. Crosstalk between metabolism and circadian clocks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019; 20: 227–241. - PubMed
-
- Serin Y, Acar Tek N. Effect of circadian rhythm on metabolic processes and the regulation of energy balance. Ann Nutr Metab 2019; 74: 322–330. - PubMed
-
- Sato A, Ohtsuka Y, Yamanaka Y. Morning mastication enhances postprandial glucose metabolism in healthy young subjects. Tohoku J Exp Med 2019; 249: 193–201. - PubMed
-
- Carroll KF, Nestel PJ. Diurnal variation in glucose tolerance and in insulin secretion in man. Diabetes 1973; 22: 333–348. - PubMed

