Transcriptome-Wide 5-Methylcytosine Functional Profiling of Long Non-Coding RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32801911
- PMCID: PMC7414925
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S262450
Transcriptome-Wide 5-Methylcytosine Functional Profiling of Long Non-Coding RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Growing evidence indicates that methylation status is associated with the pathogenesis of numerous types of cancers. Among these, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a deadly disease threatening global human health. Although 5-methylcytosine (m5C) has been identified as an important regulatory modification, its distribution in solid tumors, including HCC, remains unclear. The present study aimed to explore the distribution of m5C in HCC.
Materials and methods: Six pairs of human HCC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues were collected to analyze the transcriptome-wide m5C methylation of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). RNA MeRIP-seq was performed to identify m5C peaks on lncRNA and differences in m5C distribution between HCC and adjacent tissues. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment pathway analyses were explored to predict the possible roles of m5C.
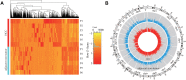
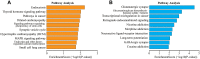
Results: Using m5C peak sequencing, we observed that a sequence motif was necessary for m5C methylation in HCC lncRNA. Unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis confirmed that lncRNA m5C methylation occurred more frequently in HCC than adjacent non-tumor tissues. RNA sequencing data demonstrated that more genes were up-regulated by methylation in HCC, while methylation down-regulated more genes in adjacent non-tumor tissues. GO and KEGG pathway analyses revealed that genes having a significant correlation with m5C sites in lncRNA were involved in HCC signaling pathways.
Conclusion: Our results revealed the substantially different amounts and distributions of m5C in HCC compared to adjacent non-tumor tissue. We further predicted the cellular functions in HCC that m5C may participate in to provide evidence implicating m5C lncRNA epigenetic regulation in the tumorigenesis and progression in HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; lncRNA; m5C; tumorigenesis.
© 2020 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct 5-methylcytosine profiles of LncRNA in breast cancer brain metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 27;25(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13948-w. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40148799 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of distinct 5-methylcytosine profiles of messenger RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma and paired adjacent non-tumor tissues.J Transl Med. 2020 Jun 22;18(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02417-6. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32571340 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct 5-methylcytosine profiles of circular RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Sep 15;12(9):5719-5729. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33042451 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into RNA m5C methylation modification in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Nov;1879(6):189223. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189223. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39577751 Review.
-
Deciphering the vital roles and mechanism of m5C modification on RNA in cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;13(12):6125-6146. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38187052 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Methylation Game: Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Dynamics of 5-Methylcytosine.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 3;10:915685. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.915685. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35721489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of main RNA modifications in cancer: N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytosine, and pseudouridine.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Apr 28;7(1):142. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01003-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35484099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal 5-methylcytosine lncRNA methylome is involved in human high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):13625-13639. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035702 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Main RNA Methylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: N6-Methyladenosine, 5-Methylcytosine, and N1-Methyladenosine.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 30;9:767668. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.767668. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34917614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the Expression Patterns and Potential Prognostic Role of 5-Methylcytosine Regulators in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 16;10:842220. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.842220. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252205 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

