Pretreatment hemoglobin level as a prognostic factor in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32802001
- PMCID: PMC7413985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.07.002
Pretreatment hemoglobin level as a prognostic factor in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: Evaluate pretreatment hemoglobin values as a prognostic factor in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
Background: Anemia is one of the most prevalent laboratory abnormalities in oncological disease. It leads to a decrease in cellular oxygen supply, altering radiosensitivity of tumor cells and compromising therapeutic outcomes.
Materials and methods: Retrospective evaluation of patients with HNSCC treated with cCRT. Primary and secondary endpoint was to evaluate the correlation of Hb levels (≥12.5 g/dL or <12.5 g/dL) at the beginning of cCRT with overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), respectively.
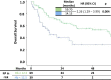
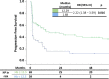
Results: A total of 108 patients were identified. With a median follow-up of 16.10 months median OS was 59.70 months for Hb ≥12.5 g/dL vs. 14.13 months for Hb <12.5 g/dL (p = 0.004). PFS was 12.29 months for Hb ≥12.5 g/dL and 1.68 months for Hb <12.5 g/dL (p = 0.016).
Conclusions: In this analysis, Hb ≥12.5 g/dL correlated with significantly better OS and PFS. Further studies are needed to validate these findings.
Keywords: Anemia; Biomarkers; Chemoradiotherapy; Head and neck neoplasms; Hemoglobin.
© 2020 Greater Poland Cancer Centre. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonged radiation time and low nadir hemoglobin during postoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy are both poor prognostic factors with synergistic effect on locally advanced head and neck cancer patients.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Jan 28;8:251-8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S70204. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 25670907 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment anemia is correlated with the reduced effectiveness of radiation and concurrent chemotherapy in advanced head and neck cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Mar 15;61(4):1087-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.07.710. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 15752888
-
Chemoradiation of unresectable pancreatic carcinoma: impact of pretreatment hemoglobin level on patterns of failure.Strahlenther Onkol. 2003 Feb;179(2):87-92. doi: 10.1007/s00066-003-1043-y. Strahlenther Onkol. 2003. PMID: 12590318
-
Concurrent cisplatin or cetuximab with radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 4;99(36):e21785. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021785. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32899005 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with weekly versus triweekly cisplatin in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Comparative analysis.Head Neck. 2019 May;41(5):1490-1498. doi: 10.1002/hed.25379. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Head Neck. 2019. PMID: 30835900
Cited by
-
Quantitative Metabolomics to Explore the Role of Plasma Polyamines in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):101. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010101. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613539 Free PMC article.
-
A predictive survival model for patients with stage IV oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiation.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jan;281(1):369-377. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08187-3. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37594545
-
The Impact of YRNAs on HNSCC and HPV Infection.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 23;11(3):681. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030681. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979661 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Drugs for Chemotherapy- and Cancer-Related Anemia.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 24;13:593-611. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S262349. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34194245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment peripheral blood biomarkers in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemo/bioradiotherapy.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 May 5. doi: 10.1007/s12094-025-03897-y. Online ahead of print. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40323571
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Fitzmaurice C., Allen C., Barber R.M. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of life lost, Years lived with Disability and Disability-adjusted life years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McCloskey S.A., Jaggernauth W., Rigual N.R. Radiation treatment interruptions greater than one week and low hemoglobin levels (12 g/dL) are predictors of local regional failure after definitive concurrent chemotherapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol. 2009;32(6):587–591. - PubMed
-
- Forastiere A.A., Goepfert H., Maor M. Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for organ preservation in advanced laryngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(22):2091–2098. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

