Buyang Huanwu Decoction Promotes Angiogenesis after Cerebral Ischemia by Inhibiting the Nox4/ROS Pathway
- PMID: 32802129
- PMCID: PMC7415092
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5264205
Buyang Huanwu Decoction Promotes Angiogenesis after Cerebral Ischemia by Inhibiting the Nox4/ROS Pathway
Abstract
Background: Buyang Huanwu decoction (BYHWD), an important traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has been used clinically for centuries for the treatment of various diseases. The study aims to explore the BYHWD effects on angiogenesis and neuroprotection after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (CI/R) injury in rats and to explore the underlying angiogenic roles and mechanisms of BYHWD in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) model.
Methods: The effects of BYHWD on neurological function were screened by measuring neurological deficits, spatial memory function, and angiogenesis (by microvascular density (MVD) and cerebral blood flow (CBF)) after CI/R injury in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in vivo in rats. In vitro, we examined the angiogenic roles and mechanisms of action of BYHWD in an H2O2-induced oxidative stress HUVECs model by measuring cell viability, apoptosis, vascular tube formation, intracellular ROS generation, NADPH oxidase (Nox) activity, and Nox4 protein expression.
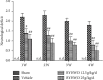
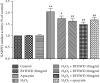
Results: BYHWD significantly improved neurological function, including neurological deficits and spatial learning and memory, and significantly increased MVD and CBF in the ischemic penumbra after CI/R injury in rats. BYHWD significantly increased cell viability, inhibited apoptosis, induced vascular tube formation, decreased intracellular ROS generation, and reduced Nox activity and Nox4 protein expression in H2O2-treated HUVECs in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that BYHWD promotes neurological function recovery and increases angiogenesis. BYHWD exerts angiogenic effects against cerebral ischemic injury through the downregulation of Nox4, which results in the reduction of ROS generation.
Copyright © 2020 Jian Shen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Hu Y., Li R., Yang H., Luo H., Chen Z. Sirtuin 6 is essential for sodium sulfidemediated cytoprotective effect in ischemia/reperfusion-stimulated brain endothelial cells. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2015;24(3):601–609. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jung Y. S., Lee S. W., Park J. H., Seo H. B., Choi B. T., Shin H. K. Electroacupuncture preconditionin reduces ROS generation with Nox4 down-regulation and ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke. Journal of Biomedical Science. 2016;23:p. 32. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0249-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

