CT-TEE Image Registration for Surgical Navigation of Congenital Heart Disease Based on a Cycle Adversarial Network
- PMID: 32802148
- PMCID: PMC7352142
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4942121
CT-TEE Image Registration for Surgical Navigation of Congenital Heart Disease Based on a Cycle Adversarial Network
Abstract
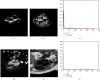
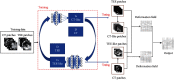
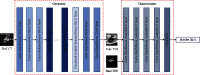
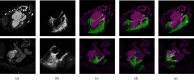
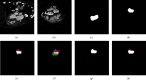
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) has become an essential tool in interventional cardiologist's daily toolbox which allows a continuous visualization of the movement of the visceral organ without trauma and the observation of the heartbeat in real time, due to the sensor's location at the esophagus directly behind the heart and it becomes useful for navigation during the surgery. However, TEE images provide very limited data on clear anatomically cardiac structures. Instead, computed tomography (CT) images can provide anatomical information of cardiac structures, which can be used as guidance to interpret TEE images. In this paper, we will focus on how to transfer the anatomical information from CT images to TEE images via registration, which is quite challenging but significant to physicians and clinicians due to the extreme morphological deformation and different appearance between CT and TEE images of the same person. In this paper, we proposed a learning-based method to register cardiac CT images to TEE images. In the proposed method, to reduce the deformation between two images, we introduce the Cycle Generative Adversarial Network (CycleGAN) into our method simulating TEE-like images from CT images to reduce their appearance gap. Then, we perform nongrid registration to align TEE-like images with TEE images. The experimental results on both children' and adults' CT and TEE images show that our proposed method outperforms other compared methods. It is quite noted that reducing the appearance gap between CT and TEE images can benefit physicians and clinicians to get the anatomical information of ROIs in TEE images during the cardiac surgical operation.
Copyright © 2020 Yunfei Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Radford A., Metz L., Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

