Epigenetic repression of miR-17 contributed to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-triggered insulin resistance by targeting Keap1-Nrf2/miR-200a axis in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 32802189
- PMCID: PMC7415800
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.45253
Epigenetic repression of miR-17 contributed to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-triggered insulin resistance by targeting Keap1-Nrf2/miR-200a axis in skeletal muscle
Abstract
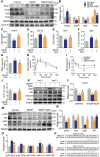
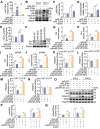
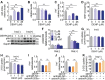
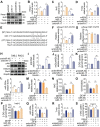
Rationale: Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is detectable before type 2 diabetes is diagnosed. Exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), a typical environmental endocrine-disrupting chemical, is a novel risk factor for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. This study aimed to explore insulin signaling regulatory pathway in skeletal muscle of the DEHP-induced insulin-resistant mice and to investigate potential therapeutic strategies for treating insulin resistance. Methods: C57BL/6J male mice were exposed to 2 mg/kg/day DEHP for 15 weeks. Whole-body glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress and deregulated miRNA-mediated molecular transduction in skeletal muscle were examined. microRNA (miRNA) interventions based on lentiviruses and adeno-associated viruses 9 (AAV9) were performed. Results: Dnmt3a-dependent promoter methylation and lncRNA Malat1-related sponge functions cooperatively downregulated miR-17 in DEHP-exposed skeletal muscle cells. DEHP suppressed miR-17 to disrupt the Keap1-Nrf2 redox system and to activate oxidative stress-responsive Txnip in skeletal muscle. Oxidative stress upregulated miR-200a, which directly targets the 3'UTR of Insr and Irs1, leading to hindered insulin signaling and impaired insulin-dependent glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, ultimately promoting the development of insulin resistance. AAV9-induced overexpression of miR-17 and lentivirus-mediated silencing of miR-200a in skeletal muscle ameliorated whole-body insulin resistance in DEHP-exposed mice. Conclusions: The miR-17/Keap1-Nrf2/miR-200a axis contributed to DEHP-induced insulin resistance. miR-17 is a positive regulator, whereas miR-200a is a negative regulator of insulin signaling in skeletal muscle, and both miRNAs have the potential to become therapeutic targets for preventing and treating insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Environmental endocrine-disrupting chemical; Insulin resistance; Oxidative stress; Skeletal muscle; microRNA.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-200a improves diabetic endothelial dysfunction by targeting KEAP1/NRF2.J Endocrinol. 2020 Apr;245(1):129-140. doi: 10.1530/JOE-19-0414. J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32031966
-
Overexpression of miR-200a protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis by modulating the kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling axis.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Oct;38(4):1303-11. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2719. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27573160
-
Upregulation of microRNA-200a in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances the repair of spinal cord injury in rats by reducing oxidative stress and regulating Keap1/Nrf2 pathway.Artif Organs. 2020 Jul;44(7):744-752. doi: 10.1111/aor.13656. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Artif Organs. 2020. PMID: 31995644
-
Epigenetic regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):337-349. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26117320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 May;1865(5):721-733. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29499228 Review.
Cited by
-
Phthalate and gallstones: the mediation of insulin.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 5;12:1401420. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1401420. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38903577 Free PMC article.
-
DLRAPom: a hybrid pipeline of Optimized XGBoost-guided integrative multiomics analysis for identifying targetable disease-related lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory axes.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Mar 10;23(2):bbac046. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac046. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35224615 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of 4-tert-Butylphenol on Inflammation and Glycogen Metabolism in Cyprinus carpio L via the miR-363/PKCδ Axis.Environ Health (Wash). 2025 Feb 13;3(5):539-550. doi: 10.1021/envhealth.4c00242. eCollection 2025 May 16. Environ Health (Wash). 2025. PMID: 40400550 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of urinary biomarkers of phthalates, phenols, parabens, and organophosphate esters with glycemic traits in pregnancy: The Healthy Start Study.Environ Res. 2024 Dec 1;262(Pt 1):119810. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119810. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 39155036
-
Inappropriately sweet: Environmental endocrine-disrupting chemicals and the diabetes pandemic.Adv Pharmacol. 2021;92:419-456. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2021.04.002. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Adv Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34452693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dales RE, Kauri LM, Cakmak S. The associations between phthalate exposure and insulin resistance, beta-cell function and blood glucose control in a population-based sample. Sci Total Environ. 2018;612:1287–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

