Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Primary Amines Using Geobacillus stearothermophilus Amine Dehydrogenase Variant
- PMID: 32802214
- PMCID: PMC7422701
- DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201902085
Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Primary Amines Using Geobacillus stearothermophilus Amine Dehydrogenase Variant
Abstract
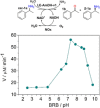
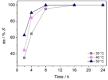
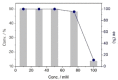
A NADH-dependent engineered amine dehydrogenase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus (LE-AmDH-v1) was applied together with a NADH-oxidase from Streptococcus mutans (NOx) for the kinetic resolution of pharmaceutically relevant racemic α-chiral primary amines. The reaction conditions (e. g., pH, temperature, type of buffer) were optimised to yield S-configured amines with up to >99 % ee.
Keywords: amine dehydrogenases; biocatalysis; kinetic resolution; oxidative deamination; α-chiral amines.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation of Oxidoreductases with Dual Alcohol Dehydrogenase and Amine Dehydrogenase Activity.Chemistry. 2021 Feb 15;27(10):3315-3325. doi: 10.1002/chem.202003140. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 33073866 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of amine dehydrogenases with increased catalytic performance and substrate scope from ε-deaminating L-Lysine dehydrogenase.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 16;10(1):3717. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11509-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31420547 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing cofactor recycling in the bioconversion of racemic alcohols to chiral amines with alcohol dehydrogenase and amine dehydrogenase by coupling cells and cell-free system.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019 Mar;116(3):536-542. doi: 10.1002/bit.26896. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019. PMID: 30536736
-
Microbial/enzymatic synthesis of chiral drug intermediates.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2000;47:33-78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(00)47001-2. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 12876794 Review.
-
Recent achievements in developing the biocatalytic toolbox for chiral amine synthesis.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014 Apr;19:180-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24721252 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of Oxidoreductases with Dual Alcohol Dehydrogenase and Amine Dehydrogenase Activity.Chemistry. 2021 Feb 15;27(10):3315-3325. doi: 10.1002/chem.202003140. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 33073866 Free PMC article.
-
High coenzyme affinity chimeric amine dehydrogenase based on domain engineering.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022 Mar 27;9(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00528-0. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022. PMID: 38647888 Free PMC article.
-
An Update: Enzymatic Synthesis for Industrial Applications.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Jul;64(27):e202505976. doi: 10.1002/anie.202505976. Epub 2025 May 16. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40241335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Trends and Future Opportunities in the Enzymatic Formation of C-C, C-N, and C-O bonds.Chembiochem. 2022 Mar 18;23(6):e202100464. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100464. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34726813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- None
-
- Wittcoff H. A., Rueben B. G., Plotkin J. S., Industrial Organic Chemicals, 2nd ed., Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2004;
-
- Ghislieri D., Turner N. J., Top. Catal. 2013, 57, 284–300;
-
- Constable D. J. C., Dunn P. J., Hayler J. D., Humphrey G. R., Leazer J. J. L., Linderman R. J., Lorenz K., Manley J., Pearlman B. A., Wells A., Zaks A., Zhang T. Y., Green Chem. 2007, 9, 411–420;
-
- Nugent T. C., Chiral amine synthesis: Methods, Developments and Applications, Wiley-VCH, 2010.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
