MicroRNA-375-mediated regulation of ILC2 cells through TSLP in allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 32802247
- PMCID: PMC7419668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100451
MicroRNA-375-mediated regulation of ILC2 cells through TSLP in allergic rhinitis
Abstract
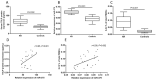
Background: Studies have shown that the number and function of type II innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) in peripheral blood of allergic rhinitis (AR) children increased significantly. This study aims to evaluate the role of miR-375 in the regulation of the differentiation and function of ILC2 through both in vivo and in vitro studies.
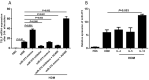
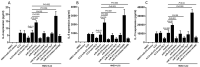
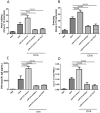
Methods: The expression of miR-375, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and the frequency of ILC2 were detected and compared between AR children and controls by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbnent assay (ELISA) and flow cytometry, respectively. The miR-375 mimics or inhibitors were transfected into human nasal epithelial cells (HNECs), and the production of TSLP was detected by ELISA. HNECs and ILC2s were co-cultured to explore the role of miR-375 on ILC2s. AR mice models were established to prove the effect of miR-375 on ILC2s in vivo.
Results: The expression of TSLP, miR-375, and the frequency of ILC2 were significantly higher in AR compared with controls. We found that the TSLP expression by HNECs were significantly higher when transfected with miR-375 mimics than in those transfected with miR-control and miR-375 inhibitor. In the coculture system, HNECs transfected with miR-375 mimics promote the type II cytokines production by ILC2, and this effect was blocked by anti-TSLP. Our results also showed that the miR-375 inhibitors attenuate allergic symptoms and production of type II cytokines in AR mice.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that miR-375-mediated regulation of ILC2 cells through TSLP, providing new potential treatment target for AR.
Keywords: AR, Allergic rhinitis; Allergic rhinitis; ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbnent assay; HNECs; HNECs, Human nasal epithelial cells; ILC2, Type II innate lymphoid cells; ILC2s; PCR, Real-time polymerase chain reaction; TSLP, Thymic stromal lymphopoietin; miR-375.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opposing roles of IL-17A and IL-25 in the regulation of TSLP production in human nasal epithelial cells.Allergy. 2010 May;65(5):581-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02252.x. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Allergy. 2010. PMID: 19968632
-
The Effect of IL-35 on the Expression of Nasal Epithelial-Derived Proinflammatory Cytokines.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Dec 3;2021:1110671. doi: 10.1155/2021/1110671. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34899052 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-155 plays critical effects on Th2 factors expression and allergic inflammatory response in type-2 innate lymphoid cells in allergic rhinitis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;23(10):4097-4109. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17911. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31173279
-
[A review on group 2 innate lymphoid cells and miR-155 in allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Dec 20;31(24):1940-1943. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.24.019. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29798323 Review. Chinese.
-
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are important in typical type 2 immune-mediated diseases and an essential therapeutic target.J Int Med Res. 2022 Jan;50(1):3000605211053156. doi: 10.1177/03000605211053156. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35048721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral Multiple Cytokine Profiles Identified CD39 as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Reflecting Disease Severity in Allergic Rhinitis Patients.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 May 10;2023:3217261. doi: 10.1155/2023/3217261. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37207043 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs and Virus and Treatment in Allergic Rhinitis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 15;2022:1979447. doi: 10.1155/2022/1979447. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9898150. doi: 10.1155/2023/9898150. PMID: 36285160 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Rhinitis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 9;17:8599-8610. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S485128. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39539728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in type 2 diseases and allergen-specific immunotherapy.Front Allergy. 2022 Sep 12;3:993937. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.993937. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 36172292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends of MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: bibliometrics and visualization analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):53-66. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07250-6. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39604743
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

