Melatonin Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Metabolic Disorder in DSS-Induced Depression Rats
- PMID: 32802257
- PMCID: PMC7415091
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1241894
Melatonin Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Metabolic Disorder in DSS-Induced Depression Rats
Abstract
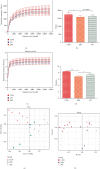
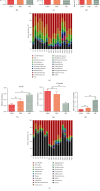
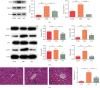
There is a bidirectional relationship between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and depression/anxiety. Emerging evidences indicate that the liver may be involved in microbiota-gut-brain axis. This experiment focused on the role of melatonin in regulating the gut microbiota and explores its mechanism on dextran sulphate sodium- (DSS-) induced neuroinflammation and liver injury. Long-term DSS-treatment increased lipopolysaccharide (LPS), proinflammation cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α, and gut leak in rats, breaking blood-brain barrier and overactivated astrocytes and microglia. Ultimately, the rats showed depression-like behavior, including reduction of sucrose preference and central time in open field test and elevation of immobility time in a forced swimming test. Oral administration with melatonin alleviated neuroinflammation and depression-like behaviors. However, melatonin supplementation did not decrease the level of LPS but increase short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production to protect DSS-induced neuroinflammation. Additionally, western blotting analysis suggested that signaling pathways farnesoid X receptor-fibroblast growth factor 15 (FXR-FGF 15) in gut and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) in the liver overactivated in DSS-treated rats, indicating liver metabolic disorder. Supplementation with melatonin markedly inhibited the activation of these two signaling pathways and its downstream p38. As for the gut microbiota, we found that immune response- and SCFA production-related microbiota, like Lactobacillus and Clostridium significantly increased, while bile salt hydrolase activity-related microbiota, like Streptococcus and Enterococcus, significantly decreased after melatonin supplementation. These altered microbiota were consistent with the alleviation of neuroinflammation and metabolic disorder. Taken together, our findings suggest melatonin contributes to reshape gut microbiota and improves inflammatory processes in the hippocampus (HPC) and metabolic disorders in the liver of DSS rats.
Copyright © 2020 Wei-jie Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Patten S. B., Beck C. A., Kassam A., Williams J. V., Barbui C., Metz L. M. Long-term medical conditions and major depression: strength of association for specific conditions in the general population. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 2016;50(4):195–202. doi: 10.1177/070674370505000402. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

