Peroxiredoxin-1 Overexpression Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis
- PMID: 32802259
- PMCID: PMC7411498
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2405135
Peroxiredoxin-1 Overexpression Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis
Abstract
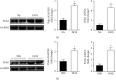
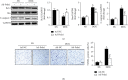
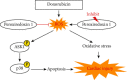
Background. Previous research has shown that peroxiredoxin 1 (Prdx1) is an important modulator of physiological and pathophysiological cardiovascular events. This study is aimed at investigating the role and underlying mechanism of Prdx1 in doxorubicin- (DOX-) induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiac-specific expression of Prdx1 was induced in mice, and the mice received a single dose of DOX (15 mg/kg) to generate cardiotoxicity. First, our study demonstrated that Prdx1 expression was upregulated in the heart and in cardiomyocytes after DOX treatment. Second, we provided direct evidence that Prdx1 overexpression ameliorated DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Mechanistically, we found that DOX treatment increased the phosphorylation level of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1) and the downstream protein p38 in the heart and in cardiomyocytes, and these effects were decreased by Prdx1 overexpression. In contrast, inhibiting Prdx1 promoted DOX-induced cardiac injury via the ASK1/p38 pathway. These results suggest that Prdx1 may be an effective therapeutic option to prevent DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Copyright © 2020 Lai Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest are declared by the authors.
Figures






References
-
- Chen Y., Huang T., Shi W., Fang J., Deng H., Cui G. Potential targets for intervention against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity based on genetic studies: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2020;138:88–98. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.11.150. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

