Olive Leaf Polyphenols Attenuate the Clinical Course of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Provide Neuroprotection by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Regulating Microglia and SIRT1, and Preserving Myelin Integrity
- PMID: 32802267
- PMCID: PMC7415106
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6125638
Olive Leaf Polyphenols Attenuate the Clinical Course of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Provide Neuroprotection by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Regulating Microglia and SIRT1, and Preserving Myelin Integrity
Abstract
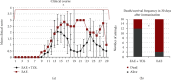
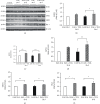
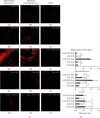
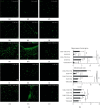
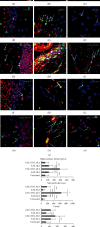
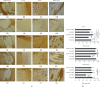
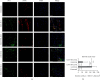
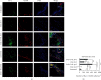
Numerous evidences suggest that plant polyphenols may have therapeutic benefits in regulating oxidative stress and providing neuroprotection in many neurodegenerative diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS). However, these mechanisms are not yet completely understood. In this study, we investigated the effect of olive leaf polyphenols on oxidative stress through oxidation marker level and activity (TBARS, SOD, and GPX) and their protein expression (SOD1, SOD2, and GPX1), as well as the protein expression of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and microglia markers (Iba-1, CD206, and iNOS) and myelin integrity (proteolipid protein expression) in the brain of rats with induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and subjected to olive leaf therapy. Experiments were performed in male EAE DA rats, which were randomly divided into 2 main groups: EAE groups treated with the therapy of olive leaf (EAE+TOL) and untreated EAE control groups. The EAE treated groups consumed olive leaf tea instead of drinking water (ad libitum) from the beginning to the end of the experiment. In addition, olive leaf extract was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) for the 10 continuous days and started on the 8th day after EAE induction. The clinical course was monitored in both groups until the 30th day after EAE induction. Our results demonstrated that TOL attenuated the clinical course of EAE; reduced the oxidative stress (by decreasing the concentration of MDA); upregulated antioxidant enzymes (SOD1, SOD2, and GPX1), SIRT1 (overall and microglial), and anti-inflammatory M2 microglia; downregulated proinflammatory M1 type; and preserved myelin integrity. These data support the idea that TOL may be an effective therapeutic approach for treating MS and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Jasminka Giacometti and Tanja Grubić-Kezele.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adamczyk B., Niedziela N., Adamczyk-Sowa M. Novel approaches of oxidative stress mechanisms in the multiple sclerosis pathophysiology and therapy. In: Zagon I. S., McLaughlin P. J., editors. Multiple Sclerosis: Perspectives in Treatment and Pathogenesis. Brisbane, Australia: Codon Publications; 2017. pp. 155–171. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

