Method development for cross-study microbiome data mining: Challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 32802279
- PMCID: PMC7419250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.07.020
Method development for cross-study microbiome data mining: Challenges and opportunities
Abstract
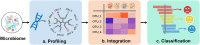
During the past decade, tremendous amount of microbiome sequencing data has been generated to study on the dynamic associations between microbial profiles and environments. How to precisely and efficiently decipher large-scale of microbiome data and furtherly take advantages from it has become one of the most essential bottlenecks for microbiome research at present. In this mini-review, we focus on the three key steps of analyzing cross-study microbiome datasets, including microbiome profiling, data integrating and data mining. By introducing the current bioinformatics approaches and discussing their limitations, we prospect the opportunities in development of computational methods for the three steps, and propose the promising solutions to multi-omics data analysis for comprehensive understanding and rapid investigation of microbiome from different angles, which could potentially promote the data-driven research by providing a broader view of the "microbiome data space".
Keywords: Amplicon sequencing; Data mining; Microbiome; Microbiome search; Multi-omics data; Shotgun metagenome.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
