A new standardized data collection system for brain stereotactic external radiotherapy: the PRE.M.I.S.E project
- PMID: 32802398
- PMCID: PMC7421993
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2020-0015
A new standardized data collection system for brain stereotactic external radiotherapy: the PRE.M.I.S.E project
Abstract
Background: In recent years, novel radiation therapy techniques have moved clinical practice toward tailored medicine. An essential role is played by the decision support system, which requires a standardization of data collection. The Aim of the Prediction Models In Stereotactic External radiotherapy (PRE.M.I.S.E.) project is the implementation of systems that analyze heterogeneous datasets. This article presents the project design, focusing on brain stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT).
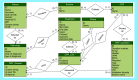
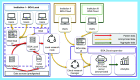
Materials & methods: First, raw ontology was defined by exploiting semiformal languages (block and entity relationship diagrams) and the natural language; then, it was transposed in a Case Report Form, creating a storage system.
Results: More than 130 brain SRT's variables were selected. The dedicated software Beyond Ontology Awareness (BOA-Web) was set and data collection is ongoing.
Conclusion: The PRE.M.I.S.E. project provides standardized data collection for a specific radiation therapy technique, such as SRT. Future aims are: including other centers and validating an extracranial SRT ontology.
Keywords: big data; brain; personalized medicine; predictive model; stereotactic.
© 2020 Silvia Longo.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in, or financial conflict, with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Alitto A, Gatta R, Vanneste B. et al. PRODIGE: prediction models in prostate cancer for personalized medicine challenge. Future Oncol. 13(24), 2171–2181 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Valentini V, Dinapoli N, Damiani A. The future of predictive models in radiation oncology: from extensive data mining to reliable modeling of the results. Future Oncol. 9(3), 311–313 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Tagliaferri L, Kovács G, Autorino R. et al. ENT COBRA (Consortium for Brachytherapy Data Analysis): interdisciplinary standardized data collection system for head and neck patients treated with interventional radiotherapy (brachytherapy). J. Contemp. Brachytherapy 8(4), 336–343 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gruber TR. A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowledge Acquisition 5(2), 199–220 (1993).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
