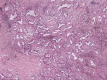
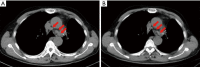
First-line treatment selection with organoids of an EGFR m + TP53 m stage IA1 patient with early metastatic recurrence after radical surgery and follow-up
- PMID: 32802455
- PMCID: PMC7399434
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-20-1882
First-line treatment selection with organoids of an EGFR m + TP53 m stage IA1 patient with early metastatic recurrence after radical surgery and follow-up
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd-20-1882). ZJ reports grants from Beijing Students’ platform for innovation and entrepreneurship training program, during the conduct of the study. ZC reports personal fees from Accurate International Biotechnology Co. Ltd, during the conduct of the study. MH reports personal fees from Accurate International Biotechnology Co. Ltd., during the conduct of the study. YY reports personal fees from Accurate International Biotechnology Co. Ltd, during the conduct of the study. HHZ reports personal fees from Burning Rock Biotechnology Co. Ltd., during the conduct of the study. JS reports personal fees from Burning Rock Biotechnology Co. Ltd., during the conduct of the study. DCC reports personal fees, non-financial support and other from AstraZeneca, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Bayer, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Boehringer-Ingelheim, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Chugai, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Merck, Sharp & Dohme, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Novartis, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Pfizer, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Roche, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Takeda, outside the submitted work. AP reports personal fees from Roche, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from MSD, personal fees from Lilly, personal fees from Dako, personal fees from Astra Zeneca, outside the submitted work, and he serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Aug 2019 to Jul 2021. CG reports personal fees from Astra Zeneca, grants and personal fees from MSD, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from Roche, personal fees from Menarini, personal fees from Novartis, outside the submitted work. NL reports grants from Beijing Natural Science Foundation, grants from Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (MOST), grants from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Young Medical Talent Award Fund, grants from Beijing Students’ platform for innovation and entrepreneurship training program, grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China Grant, during the conduct of the study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Comment in
-
Treatment strategy of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Mar;14(3):602-606. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-177. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35399242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment selection with organoids in an EGFRm + TP53m stage IA1 patient with recurrence after radical surgery.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Mar;14(3):595-598. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-64. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35399248 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Future prospects of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and surgery for non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):809-811. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-57. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multidisciplinary and real life data: practical management of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):805-808. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-181. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572878 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intratumoral and intertumoral heterogeneity drives EGFR treatment considerations.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1299-1301. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-312. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Critical points in the management of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1748-1752. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-269. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The emerging landscape of EFGR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma-successes and challenges.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1766-1771. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-432. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
