Ear Molding Therapy: Laypersons' Perceptions, Preferences, and Satisfaction with Treatment Outcome
- PMID: 32802642
- PMCID: PMC7413762
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002902
Ear Molding Therapy: Laypersons' Perceptions, Preferences, and Satisfaction with Treatment Outcome
Abstract
This study investigates laypersons' perceptions of congenital ear deformities and preferences for treatment, particularly with ear molding therapy-an effective, noninvasive, yet time-sensitive treatment.
Methods: Laypersons were recruited via crowdsourcing to view photographs of normal ears or one of the following ear deformities, pre- and post-molding: constricted, cryptotia, cupped/lopped, helical rim deformity, prominent, and Stahl. Participants answered questions regarding perceptions and treatment preferences for the ear. Statistical analyses included multiple linear and logistic regressions and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests.
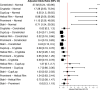
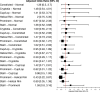
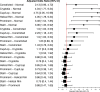
Results: A total of 983 individuals participated in the study. All deformities were perceived as significantly abnormal, likely to impair hearing, and associated with lower psychosocial quality of life (all P < 0.001). For all deformities, participants were likely to choose ear molding over surgery despite the logistical and financial implications of ear molding (all P < 0.02). Participants were significantly more satisfied with the outcome of ear molding in all deformities compared with control, except constricted ears (all P < 0.002, except Pconstricted = 0.073). Concern for hearing impairment due to ear deformity was associated with increased likelihoods of seeing a physician (P < 0.001) and choosing ear molding despite treatment logistics and costs (all P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Laypersons perceived all ear deformities as abnormal and associated with low psychosocial quality of life. Despite logistical and financial implications, laypersons generally desired molding therapy for ear deformities; treatment outcomes were satisfactory for all deformities except constricted ears. Timely diagnosis of this condition is crucial to reaping the benefits of ear molding therapy.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures








References
-
- Porter CJ, Tan ST. Congenital auricular anomalies: topographic anatomy, embryology, classification, and treatment strategies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:1701–1712. - PubMed
-
- Chang CS, Bartlett SP. Deformations of the ear and their nonsurgical correction. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2019;58:798–805. - PubMed
-
- Tanzer RC. The constricted (cup and lop) ear. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975;55:406–415 - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Jiang H, Yang Q, et al. Microtia in a Chinese specialty clinic population: clinical heterogeneity and associated congenital anomalies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;142:892e–903e. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
