Intraoperative Autoderm Decontamination for Use in Immediate Single-stage Direct-to-implant Breast Reconstruction
- PMID: 32802661
- PMCID: PMC7413811
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002968
Intraoperative Autoderm Decontamination for Use in Immediate Single-stage Direct-to-implant Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
Acellular dermal matrix (ADM) in direct-to-implant breast cancer reconstruction is the standard of care due to superior cosmetic results and decreased capsular contracture, but can be cost prohibitive. Although more economical, using patient's own dermis ("Autoderm") instead of ADM has undescribed sterility. Sterility is essential, as bacterial contamination may cause infection and capsular contraction. This study aimed to determine the sterility and optimal decontamination protocol of Autoderm.
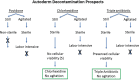
Methods: A prospective controlled study of 140 samples from 20 DIEP (deep inferior epigastric perforator) breast cancer reconstruction patients was performed. Seven de-epithelialized dermal samples (2 × 1 cm) per patient were collected from excess abdominal tissue (6 decontamination protocols and one control). Samples were submerged in povidone-iodine, chlorhexidine, or cefazolin/tobramycin/bacitracin for 15 minutes; half of the samples were agitated (150 rpm) for 15 minutes, and half were not. The control was normal saline without agitation. The solution was removed, and the tissue was sent for aerobic colony count cultures. Patient's demographic data and complications were also collected.
Results: Of 140 samples, 3 of 20 non-agitated povidone-iodine and 1 of 20 control samples had aerobic bacterial growth. All of the other 100 samples from 5 experimental groups (povidone-iodine + agitation, chlorhexidine ± agitation, and cefazolin/tobramycin/bacitracin ± agitation) had no aerobic bacterial growth.
Conclusions: This study suggests povidone-iodine + agitation, chlorhexidine ± agitation, and cefazolin/tobramycin/bacitracin ± agitation are effective at sterilizing de-epithelialized dermis, whereas povidone-iodine without agitation and saline are ineffective. Autoderm with the appropriate decontamination protocol may be a potential sterile alternative to ADM.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bostwick Autoderm and Implant Technique: Improved Outcomes for Obese Patients in Immediate Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021 Feb 1;147(2):187e-195e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007515. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021. PMID: 33165289
-
The effect of intraoperative immersion solutions on acellular dermal matrix: Biofilm formation and mechanical property.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023 Sep;84:191-202. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2023.05.025. Epub 2023 May 19. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023. PMID: 37339544
-
A comparison of five treatment protocols for contaminated bone grafts in reference to sterility and cell viability.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011 Mar 2;93(5):439-44. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00418. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011. PMID: 21368075
-
Implants and Breast Pocket Irrigation: Outcomes of Antibiotic, Antiseptic, and Saline Irrigation.Aesthet Surg J. 2022 Jan 12;42(2):NP102-NP111. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjab181. Aesthet Surg J. 2022. PMID: 33836057
-
Alloplastic adjuncts in breast reconstruction.Gland Surg. 2016 Apr;5(2):158-73. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.06.02. Gland Surg. 2016. PMID: 27047784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autoderm in Direct-to-implant Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction Decreases Perioperative Complication Rates and Improves Reconstructive Outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 May 6;13(5):e6722. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006722. eCollection 2025 May. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40330162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sobti N, Ji E, Brown RL, et al. Evaluation of acellular dermal matrix efficacy in prosthesis-based breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141:541–549. - PubMed
-
- Wazir U, Mokbel K. The evolving role of pre-pectoral ADM-assisted implant-based immediate breast reconstruction following skin-sparing mastectomy. Am J Surg. 2018;216:639–640. - PubMed
-
- Zenn M, Venturi M, Pittman T, et al. Optimizing outcomes of postmastectomy breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: a review of recent clinical data. Eplasty. 2017;17:e18 Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28663773. Accessed November 21, 2018. - PMC - PubMed
-
- JoAnna Nguyen T, Carey JN, Wong AK. Use of human acellular dermal matrix in implant-based breast reconstruction: evaluating the evidence. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:1553–1561. - PubMed
-
- Andrew Salzberg C, Ashikari AY, Michael Koch R, et al. An 8-year experience of direct-to-implant immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular dermal matrix (Alloderm). Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127:514. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources