High-resolution NU-WRF simulations of a deep convective-precipitation system during MC3E: Further improvements and comparisons between Goddard microphysics schemes and observations
- PMID: 32802697
- PMCID: PMC7427821
- DOI: 10.1002/2015JD023986
High-resolution NU-WRF simulations of a deep convective-precipitation system during MC3E: Further improvements and comparisons between Goddard microphysics schemes and observations
Abstract
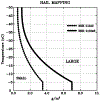
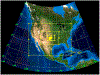
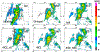
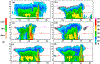
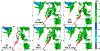
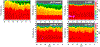
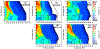
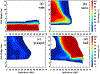
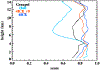
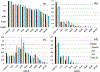
The Goddard microphysics was recently improved by adding a fourth ice class (frozen drops/hail). This new 4ICE scheme was developed and tested in the Goddard Cumulus Ensemble (GCE) model for an intense continental squall line and a moderate, less organized continental case. Simulated peak radar reflectivity profiles were improved in intensity and shape for both cases, as were the overall reflectivity probability distributions versus observations. In this study, the new Goddard 4ICE scheme is implemented into the regional-scale NASA Unified-Weather Research and Forecasting (NU-WRF) model, modified and evaluated for the same intense squall line, which occurred during the Midlatitude Continental Convective Clouds Experiment (MC3E). NU-WRF simulated radar reflectivities, total rainfall, propagation, and convective system structures using the 4ICE scheme modified herein agree as well as or significantly better with observations than the original 4ICE and two previous 3ICE (graupel or hail) versions of the Goddard microphysics. With the modified 4ICE, the bin microphysics-based rain evaporation correction improves propagation and in conjunction with eliminating the unrealistic dry collection of ice/snow by hail can replicate the erect, narrow, and intense convective cores. Revisions to the ice supersaturation, ice number concentration formula, and snow size mapping, including a new snow breakup effect, allow the modified 4ICE to produce a stronger, better organized system, more snow, and mimic the strong aggregation signature in the radar distributions. NU-WRF original 4ICE simulated radar reflectivity distributions are consistent with and generally superior to those using the GCE due to the less restrictive domain and lateral boundaries.
Figures

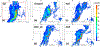
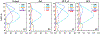
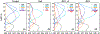
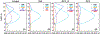
References
-
- Adams-Selin RD, van den Heever SC, and Johnson RH (2013a), Impact of graupel parameterization schemes on idealized bow echo simulations, Mon. Weather Rev, 141, 1241–1262.
-
- Adams-Selin RD, van den Heever SC, and Johnson RH (2013b), Quantitative evaluation of bow echo microphysical sensitivity, Weather Forecasting, 28, 1188–1209.
-
- Brandes EA, Ikeda K, Zhang G, Schönhuber M, and Rasmussen RM (2007), A statistical and physical description of hydrometeor distributions in Colorado snowstorms using a video disdrometer, J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol, 46, 634–650, doi: 10.1175/JAM2489.1. - DOI
-
- Bryan GH, and Morrison H (2012), Sensitivity of a simulated squall line to horizontal resolution and parameterization of microphysics, Mon. Weather Rev, 140, 202–225.
-
- Chern J-D, Tao W-K, Lang SE, Matsui T, Li J-LF, Mohr KI, Skofronick-Jackson GM, and Peters-Lidard CD (2016), Performance of the Goddard multiscale modeling framework with Goddard ice microphysical schemes, J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst, 7, doi: 10.1002/2015MS000469. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
