Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2019
- PMID: 32802702
- PMCID: PMC7387396
- DOI: 10.1007/s13340-020-00439-5
Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2019
Keywords: Diabetes; Diagnosis; Guideline; Treatment.
Figures



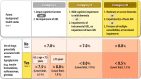
References
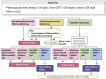
1. Guideline for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
-
- Kosaka K, Akanuma Y, Goto Y, et al. Report of Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 1982;25:859–866.
-
- World Health Organization. Report of a WHO consultation: definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance. 1999. http://www.staff.ncl.ac.uk/philip.home/who_dmc.htm.
-
- Kuzuya T, Nakagawa S, Satoh J, et al. Report of the Committee of Japan Diabetes Society on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 1999;42:385–404.
-
- American Diabetes Association Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1):S13–S27. - PubMed
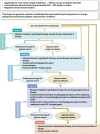
2. Goals and strategies for diabetes management
-
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group: Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Look ARG, Gregg EW, Jakicic JM, et al. Association of the magnitude of weight loss and changes in physical fitness with long-term cardiovascular disease outcomes in overweight or obese people with type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4:913–921. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sone H, Tanaka S, Tanaka S, et al. Serum level of triglycerides is a potent risk factor comparable to LDL cholesterol for coronary heart disease in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: subanalysis of the Japan Diabetes Complications Study (JDCS) J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:3448–3456. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Group JDS et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:951–964. - PubMed
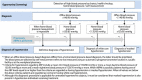
3. Medical nutrition therapy (MNT)
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1343–50 [level 1] - PubMed
-
- Terranova CO, Brakenridge CL, Lawler SP, et al. Effectiveness of lifestyle-based weight loss interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:371–8 [level 1] - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Pei JH, Kuang J, et al. Effect of lifestyle intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2015;64:338–47 [level 1] - PubMed
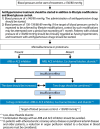
4. Physical activity/exercise
-
- Umpierre D, Ribeiro PA, Kramer CK, et al. Physical activity advice only or structured exercise training and association with HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;305:1790–9 [level 1+] - PubMed
-
- Boulé NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, et al. Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA. 2001;286:1218–27 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Pai LW, Li TC, Hwu YJ, et al. The effectiveness of regular leisure-time physical activities on long-term glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;113:77–85 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Boniol M, Dragomir M, Autier P, et al. Physical activity and change in fasting glucose and HbA1c: a quantitative meta-analysis of randomized trials. Acta Diabetol. 2017;54:983–91 [level 1+] - PubMed
-
- MacLeod SF, Terada T, Chahal BS, et al. Exercise lowers postprandial glucose but not fasting glucose in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of studies using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2013;29:593–603 [level 2] - PubMed
5. Treatment with glucose-lowering agents (excluding insulin)
-
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352:837–53. - PubMed
-
- Bennett WL, Wilson LM, Bolen S, et al. Oral diabetes medications for adults with type 2 diabetes: an update. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), Rockville (MD); 2011.
-
- Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352:854–65. - PubMed
6. Insulin therapy
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group: early worsening of diabetic retinopathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998;116:874–86. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi Y, Takayama S, Ito T, et al. Clinical features of eighty-six diabetic patients with post-treatment painful neuropathy. J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 1998;41:165–170.
-
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group: United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study 24: a 6-year, randomized, controlled trial comparing sulfonylurea, insulin, and metformin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes that could not be controlled with diet therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128:165–75. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86 [level 1] - PubMed
7. Diabetes self-management education and support for the self‑management of diabetes
-
- He X, Li J, Wang B, et al. Diabetes self-management education reduces risk of all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2017;55:712–31 [level 1+] - PubMed
-
- Ismail K, Winkley K, Rabe-Hesketh S. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of psychological interventions to improve glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2004;363(9421):1589–97 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al. Behavioral programs for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:848–60 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al. Behavioral programs for type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:836–47 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Rickheim PL, Weaver TW, Flader JL, et al. Assessment of group versus individual diabetes education: a randomized study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:269–74 [level 1] - PubMed
8. Diabetic retinopathy
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, et al. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: IX. Four-year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989;107:237–43 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, et al. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: X. Four-year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 years or more. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989;107:244–9 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Younis N, Broadbent DM, Vora JP, et al. Incidence of sight-threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study: a cohort study. Lancet. 2003;361:195–200 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Misra A, Bachmann MO, Greenwood RH, et al. Trends in yield and effects of screening intervals during 17 years of a large UK community-based diabetic retinopathy screening programme. Diabet Med. 2009;26:1040–7 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86 [level 1] - PubMed
9. Diabetic nephropathy
-
- Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–992. - PubMed
-
- Horio M, Imai E, Yasuda Y, et al. GFR estimation using standardized serum cystatin C in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;61:197–203. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes C, Complications Trial Research G, Nathan DM, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86 [level 1] - PubMed
10. Diabetic neuropathy
-
- Hotta N, Toyoda R, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Kanehara, Tokyo; 1996. p. 145–54 (in Japanese).
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:956–962. - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, et al. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:341–350. - PubMed
11. Diabetic foot
-
- IWGDF Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease https://iwgdfguidelines.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/IWGDF-Guidelines-...
-
- Frykberg RG, Zgonis T, Armstrong DG, et al. Diabetic foot disorders: a clinical practice guideline (2006 revision) J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006;45:S1–S66. - PubMed
-
- Krishinan S, Nash F, Baker N, et al. Reduction in diabetic amputations over 11 years in a defined U.K. population benefits of multidisciplinary team work and continuous prospective audit. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:99–101 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Malone JM, Snyder M, Anderson G, et al. Prevention of amputation by diabetic education. Am J Surg. 1989;158:520–4 [level 1] - PubMed
12. Diabetic macroangiopathy
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, et al. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:580–591. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:951–964. - PubMed
13. Diabetes and periodontitis
-
- Takahashi K, Nishimura F, Kurihara M, et al. Subgingival microflora and antibody responses against periodontal bacteria of young Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2001;3:104–111. - PubMed
-
- Morita I, Inagaki K, Nakamura F, et al. Relationship between periodontal status and levels of glycated hemoglobin. J Dent Res. 2012;91:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Graziani F, Gennai S, Solini A, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiologic observational evidence on the effect of periodontitis on diabetes An update of the EFP-AAP review. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45:167–187. - PubMed
14. Diabetes complicated by obesity (including metabolic syndrome)
-
- Matsuzawa Y, Sakata T, Ikeda Y, et al. Guidelines for the management of obesity disease. 2006;2006:1–91.
-
- Examination Committee of Criteria for ‘Obesity Disease’ in Japan, Japan Society for the Study of Obesity; New criteria for ‘obesity disease’ in Japan. Circ J. 2002;66:987–92 - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Boyko EJ, McNeely MJ, et al. Minimum waist and visceral fat values for identifying Japanese Americans at risk for the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:120–127. - PubMed
-
- Kashihara H, Lee JS, Kawakubo K, Tamura M, Akabayashi A. Criteria of waist circumference according to computed tomography-measured visceral fat area and the clustering of cardiovascular risk factors. Circ J. 2009;73:1881–1886. - PubMed
-
- Hiuge-Shimizu A, Kishida K, Funahashi T, et al. Absolute value of visceral fat area measured on computed tomography scans and obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors in large-scale Japanese general population (the VACATION-J study) Ann Med. 2012;44:82–92. - PubMed
15. Hypertension associated with diabetes
-
- Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019) Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–1481. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Kato M, et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endcrinol. 2017;5:951–64 [level 1] - PubMed
-
- Baba S. Nifedipine and enalapril equally reduce the progression of nephropathy in hypertensive type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001;54:191–201 [level 1] - PubMed
-
- Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Lewis JB, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:542–9 [level 1] - PubMed
16. Dyslipidemia associated with diabetes
-
- Sacks FM, Hermans MP, Fioretto P, et al. Association between plasma triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and microvascular kidney disease and retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a global case-control study in 13 countries. Circulation. 2014;129:999–1008. - PubMed
-
- Heilbronn LK, Noakes M, Clifton PM. Effect of energy restriction, weight loss, and diet composition on plasma lipids and glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:889–95 [level 2] - PubMed
17. Impaired glucose metabolism in pregnancy
-
- Ray JG, O’Brien TE, Chan WS. Preconception care and the risk of congenital anomalies in the offspring of women with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. QJM. 2001;94:435–44 [level 2] - PubMed
-
- Griffin ME, Coffey M, Johnson H, et al. Universal vs. risk factor-based screening for gestational diabetes mellitus: detection rates, gestation at diagnosis and outcome. Diabet Med. 2000;17:26–32. - PubMed
18. Pediatric/adolescent diabetes
-
- ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes 2014. Nankodo, Tokyo; 2015.
-
- Ascerini C, Craig ME, de Beaufort C, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2014 compendium. Introduction. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(Suppl 20):1–3. - PubMed
-
- Craig ME, Jefferies C, Dabelea D, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2014 compendium. Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adlescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(Suppl 20):4–17. - PubMed
-
- White NH, Cleary PA, Dahms W, et al. (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Research Group). Beneficial effects of intensive therapy of diabetes during adolescence: outcomes after the conclusion of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). J Pediatr. 2001;139:804–12. - PubMed
-
- Urakami T, Morimoto S, Nitadori Y, et al. Urine glucose screening program at schools in Japan to detect children with diabetes and its outcome: incidence and clinical characteristics of childhood type 2 diabetes in Japan. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:141–145. - PubMed
20. Acute metabolic complications of diabetes, sick days, and infectious diseases
-
- Nyenwe EA, Kitabchi AE. Evidence-based management of hyperglycemic emergencies in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94:340–351. - PubMed
-
- Wolfsdorf JI, Allgrove J, Craig ME, Edge J, Glaser N, Jain V, Lee WW, Mungai LN, Rosenbloom AL, Sperling MA, Hanas R; International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(Suppl 20):154–79 - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey A, Kraut MD, Nicolaos E, et al. Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2309–2319. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes–2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S1–S157. - PubMed
21. Prevention of type 2 diabetes
-
- Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Hata J, et al. Two risk score models for predicting incident type 2 diabetes in Japan. Diabet Med. 2012;29:107–14 - PubMed
-
- Heianza Y, Arase Y, Hsieh SD, et al. Development of a new scoring system for predicting the 5 year incidence of type 2 diabetes in Japan: the Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 6 (TOPICS 6) Diabetologia. 2012;55:3213–3223. - PubMed
Appendix ① Diabetes and cancer
-
- Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:1679–1687. - PubMed
-
- Larsson SC, Orsini N, Brismar K, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2006;49:2819–2823. - PubMed
-
- Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:207–221. - PubMed
Appendix ② Diabetes and bone mineral metabolism
-
- Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Life Science publishing.
-
- Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC, et al. Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;166:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Vestergaard P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18:427–444. - PubMed
Appendix ③ Pancreas/islet transplantation
-
- Saito T, Gotoh M, Satomi S, et al. Islet transplantation using donors after cardiac death: report of the Japan Islet Transplantation Registry. Transplantation. 2010;90:740–747. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Ansite JD, et al. Single-donor, marginal-dose islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293:830–835. - PubMed
Appendix ④ Large-scale clinical trials in Japanese patients with diabetes
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
