Is it infection or rather vascular inflammation? Game-changer insights and recommendations from patterns of multi-organ involvement and affected subgroups in COVID-19
- PMID: 32803145
- PMCID: PMC7410022
- DOI: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000211
Is it infection or rather vascular inflammation? Game-changer insights and recommendations from patterns of multi-organ involvement and affected subgroups in COVID-19
Abstract
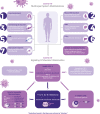
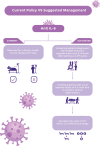
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a serious illness that has rapidly spread throughout the globe. The seriousness of complications puts significant pressures on hospital resources, especially the availability of ICU and ventilators. Current evidence suggests that COVID-19 pathogenesis majorly involves microvascular injury induced by hypercytokinemia, namely interleukin 6 (IL-6). We recount the suggested inflammatory pathway for COVID-19 and its effects on various organ systems, including respiratory, cardiac, hematologic, reproductive, and nervous organ systems, as well examine the role of hypercytokinemia in the at-risk geriatric and obesity subgroups with upregulated cytokines' profile. In view of these findings, we strongly encourage the conduction of prospective studies to determine the baseline levels of IL-6 in infected patients, which can predict a negative outcome in COVID-19 cases, with subsequent early administration of IL-6 inhibitors, to decrease the need for ICU admission and the pressure on healthcare systems. Video abstract: http://links.lww.com/CAEN/A24.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; interleukin 6; microvascular inflammation; multi-system involvement; new management strategy; repurposed use of anti-interleukin.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
