Epidermal resident γδ T cell development and function in skin
- PMID: 32803399
- PMCID: PMC11073445
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03613-9
Epidermal resident γδ T cell development and function in skin
Abstract
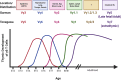
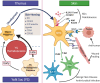
Epidermal resident γδ T cells, or dendritic epidermal T cells (DETCs) in mice, are a unique and conserved population of γδ T cells enriched in the epidermis, where they serve as the regulators of immune responses and sense skin injury. Despite the great advances in the understanding of the development, homeostasis, and function of DETCs in the past decades, the origin and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we reviewed the recent research progress on DETCs, including their origin and homeostasis in the skin, especially at transcriptional and epigenetic levels, and discuss the involvement of DETCs in skin diseases.
Keywords: Dendritic epidermal T cells (DETCs); Development; Function; Skin diseases; γδ T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest for each author.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Dendritic Epidermal T Cells in Cutaneous Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1266. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01266. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of dendritic epidermal T cells with a skewed diversity of gamma delta TCRs in V delta 1-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 1;165(7):3695-705. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.7.3695. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11034374
-
Epidermal γδ T cells originate from yolk sac hematopoiesis and clonally self-renew in the adult.J Exp Med. 2018 Dec 3;215(12):2994-3005. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181206. Epub 2018 Nov 8. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 30409784 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles of cytokine receptors in the development of epidermal gamma delta T cells.J Immunol. 2001 Aug 15;167(4):1929-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1929. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11489972
-
Functions of Vγ4 T Cells and Dendritic Epidermal T Cells on Skin Wound Healing.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1099. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01099. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing Mouse and Human Tissue-Resident γδ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 8;13:891687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.891687. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35757696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lkb1 orchestrates γδ T-cell metabolic and functional fitness to control IL-17-mediated autoimmune hepatitis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Jun;21(6):546-560. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01163-9. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38641698 Free PMC article.
-
γδ T Cells in Skin Inflammation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2022;42(5):43-56. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2022047288. Crit Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 37075018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γδ T cells: origin and fate, subsets, diseases and immunotherapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 22;8(1):434. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01653-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37989744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin γδ T Cells and Their Function in Wound Healing.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 11;13:875076. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.875076. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35479079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenner MB, et al. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986;322(6075):145–149. - PubMed
-
- Schmolka N, et al. Epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of gammadelta T cell differentiation: programming cells for responses in time and space. Semin Immunol. 2015;27(1):19–25. - PubMed
-
- Raulet DH. The structure, function, and molecular genetics of the gamma/delta T cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:175–207. - PubMed
-
- Wiest DL. Development of gammadelta T Cells, the special-force soldiers of the immune system. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1323:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

