Purinergic Signaling: Impact of GPCR Structures on Rational Drug Design
- PMID: 32803849
- PMCID: PMC8276773
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202000465
Purinergic Signaling: Impact of GPCR Structures on Rational Drug Design
Abstract
The purinergic signaling system includes membrane-bound receptors for extracellular purines and pyrimidines, and enzymes/transporters that regulate receptor activation by endogenous agonists. Receptors include: adenosine (A1 , A2A , A2B, and A3 ) and P2Y (P2Y1 , P2Y2 , P2Y4 , P2Y6 , P2Y11 , P2Y12 , P2Y13 , and P2Y14 ) receptors (all GPCRs), as well as P2X receptors (ion channels). Receptor activation, especially accompanying physiological stress or damage, creates a temporal sequence of signaling to counteract this stress and either mobilize (P2Rs) or suppress (ARs) immune responses. Thus, modulation of this large signaling family has broad potential for treating chronic diseases. Experimentally determined structures represent each of the three receptor families. We focus on selective purinergic agonists (A1 , A3 ), antagonists (A3 , P2Y14 ), and allosteric modulators (P2Y1 , A3 ). Examples of applying structure-based design, including the rational modification of known ligands, are presented for antithrombotic P2Y1 R antagonists and anti-inflammatory P2Y14 R antagonists and A3 AR agonists. A3 AR agonists are a potential, nonaddictive treatment for chronic neuropathic pain.
Keywords: drug discovery; molecular modeling; nucleosides; nucleotides; receptors.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
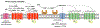


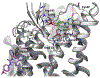
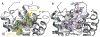
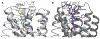
References
-
- Congreve M, de Graaf C, Swain NA, Tate CG, Cell 2020, 181, 81–91. - PubMed
-
- Novel Drug Approvals for 2019. Accessed: Dec. 29, 2019: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/new-drugs-fda-cders-new-molecular-entities-and....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

