Global alignment and assessment of TRP channel transmembrane domain structures to explore functional mechanisms
- PMID: 32804077
- PMCID: PMC7431192
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58660
Global alignment and assessment of TRP channel transmembrane domain structures to explore functional mechanisms
Abstract
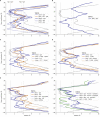
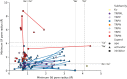
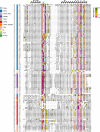
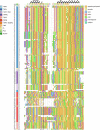
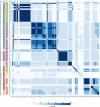
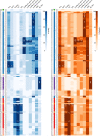
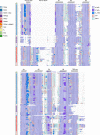
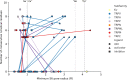
The recent proliferation of published TRP channel structures provides a foundation for understanding the diverse functional properties of this important family of ion channel proteins. To facilitate mechanistic investigations, we constructed a structure-based alignment of the transmembrane domains of 120 TRP channel structures. Comparison of structures determined in the absence or presence of activating stimuli reveals similar constrictions in the central ion permeation pathway near the intracellular end of the S6 helices, pointing to a conserved cytoplasmic gate and suggesting that most available structures represent non-conducting states. Comparison of the ion selectivity filters toward the extracellular end of the pore supports existing hypotheses for mechanisms of ion selectivity. Also conserved to varying extents are hot spots for interactions with hydrophobic ligands, lipids and ions, as well as discrete alterations in helix conformations. This analysis therefore provides a framework for investigating the structural basis of TRP channel gating mechanisms and pharmacology, and, despite the large number of structures included, reveals the need for additional structural data and for more functional studies to establish the mechanistic basis of TRP channel function.
Keywords: TRP channel; ion channel gate; membrane protein structure; molecular biophysics; none; structural alignment; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
KH, AA, AJ No competing interests declared, LF Reviewing editor, eLife, KS Senior editor, eLife
Figures


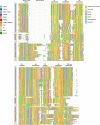
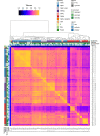
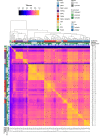
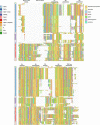
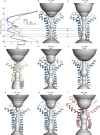






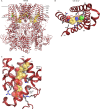


References
-
- Bae C, Anselmi C, Kalia J, Jara-Oseguera A, Schwieters CD, Krepkiy D, Won Lee C, Kim EH, Kim JI, Faraldo-Gómez JD, Swartz KJ. Structural insights into the mechanism of activation of the TRPV1 channel by a membrane-bound tarantula toxin. eLife. 2016;5:e11273. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11273. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behrendt HJ, Germann T, Gillen C, Hatt H, Jostock R. Characterization of the mouse cold-menthol receptor TRPM8 and vanilloid receptor type-1 VR1 using a fluorometric imaging plate reader (FLIPR) assay. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2004;141:737–745. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705652. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

