Discovery of a molecular glue promoting CDK12-DDB1 interaction to trigger cyclin K degradation
- PMID: 32804079
- PMCID: PMC7462607
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59994
Discovery of a molecular glue promoting CDK12-DDB1 interaction to trigger cyclin K degradation
Abstract
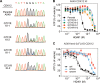
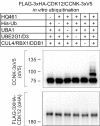
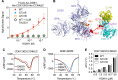
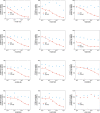
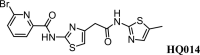
Molecular-glue degraders mediate interactions between target proteins and components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system to cause selective protein degradation. Here, we report a new molecular glue HQ461 discovered by high-throughput screening. Using loss-of-function and gain-of-function genetic screening in human cancer cells followed by biochemical reconstitution, we show that HQ461 acts by promoting an interaction between CDK12 and DDB1-CUL4-RBX1 E3 ubiquitin ligase, leading to polyubiquitination and degradation of CDK12-interacting protein Cyclin K (CCNK). Degradation of CCNK mediated by HQ461 compromised CDK12 function, leading to reduced phosphorylation of a CDK12 substrate, downregulation of DNA damage response genes, and cell death. Structure-activity relationship analysis of HQ461 revealed the importance of a 5-methylthiazol-2-amine pharmacophore and resulted in an HQ461 derivate with improved potency. Our studies reveal a new molecular glue that recruits its target protein directly to DDB1 to bypass the requirement of a substrate-specific receptor, presenting a new strategy for targeted protein degradation.
Keywords: CDK12/CCNK; biochemistry; chemical biology; human; molecular glue; target identification; targeted protein degradation.
© 2020, Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LL, PC, LC, YL, QW, JL, TH A provisional patent application (PCT/CN2020/095482) has been filed for the application of HQ461 and related small molecules as molecular glues regulating CDK12-DDB1 interaction to degrade CCNK. ZZ, YC, JW, MD, XQ No competing interests declared
Figures





































References
-
- Bajrami I, Frankum JR, Konde A, Miller RE, Rehman FL, Brough R, Campbell J, Sims D, Rafiq R, Hooper S, Chen L, Kozarewa I, Assiotis I, Fenwick K, Natrajan R, Lord CJ, Ashworth A. Genome-wide profiling of genetic synthetic lethality identifies CDK12 as a novel determinant of PARP1/2 inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Research. 2014;74:287–297. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blazek D, Kohoutek J, Bartholomeeusen K, Johansen E, Hulinkova P, Luo Z, Cimermancic P, Ule J, Peterlin BM. The cyclin K/Cdk12 complex maintains genomic stability via regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes. Genes & Development. 2011;25:2158–2172. doi: 10.1101/gad.16962311. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bussiere DE, Xie L, Srinivas H, Shu W, Burke A, Be C, Zhao J, Godbole A, King D, Karki RG, Hornak V, Xu F, Cobb J, Carte N, Frank AO, Frommlet A, Graff P, Knapp M, Fazal A, Okram B, Jiang S, Michellys PY, Beckwith R, Voshol H, Wiesmann C, Solomon JM, Paulk J. Structural basis of indisulam-mediated RBM39 recruitment to DCAF15 E3 ligase complex. Nature Chemical Biology. 2020;16:15–23. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0411-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

