Gastric Motility in Parkinson's Disease is Altered Depending on the Digestive Phase and Does Not Correlate with Patient-Reported Motor Fluctuations
- PMID: 32804102
- PMCID: PMC7683086
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-202144
Gastric Motility in Parkinson's Disease is Altered Depending on the Digestive Phase and Does Not Correlate with Patient-Reported Motor Fluctuations
Abstract
Background: Altered gastric motility is a frequent non-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease (PD). It has been hypothesized that disturbed gastric motility contributes to motor fluctuations in PD due to an erratic gastro-duodenal transport and an unpredictable absorption of drugs.
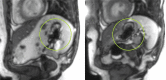
Objective: We investigated whether patient-reported fluctuations are associated with parameters of gastric motility visualized by real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the stomach.
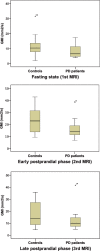
Methods: We analyzed real-time MRI-scans of the stomach after an overnight fasting period in 16 PD patients and 20 controls. MRI was performed 1) in the fasting state, 2) directly after a test meal, and 3) 4 hours postprandially. Gastric motility indices were calculated and compared between groups.
Results: MRI showed an attenuated gastric motility in PD patients compared to controls. The difference was most obvious in the early postprandial phase. Gastric motility was not associated with patient-reported motor fluctuations. Using an iron-containing capsule we were able to retrace retention of drugs in the stomach.
Conclusion: The results of this study stress the importance of considering the phase of digestion when investigating gastric motility in PD. Despite theoretical considerations, we did not find robust evidence for an association between MRI parameters of gastric motility and patient-reported motor fluctuations. For future studies that aim to investigate gastric motility in PD by MRI, we suggest multiple short-time MRIs to better track the whole gastro-duodenal phase in PD. Such an approach would also allow to retrace the retention of drugs in the stomach as shown by our approach using an iron-containing capsule.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; gastrointestinal motility; real-time magnetic resonance imaging; stomach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-time visualization of altered gastric motility by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2010 Apr 15;25(5):623-8. doi: 10.1002/mds.22841. Mov Disord. 2010. PMID: 20213819
-
The effect of subthalamic deep brain stimulation on gastric motility in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 May;26:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26952698
-
Gastric emptying in Parkinson's disease: patients with and without response fluctuations.Neurology. 1996 Apr;46(4):1051-4. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.4.1051. Neurology. 1996. PMID: 8780089
-
MRI of the stomach: a pictorial review with a focus on oncological applications and gastric motility.Abdom Imaging. 2015 Apr;40(4):907-30. doi: 10.1007/s00261-014-0251-5. Abdom Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25261256 Review.
-
Delayed gastric emptying in Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2014 Jan;29(1):23-32. doi: 10.1002/mds.25708. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Mov Disord. 2014. PMID: 24151126 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Aspirated Duodenal Fluids from Parkinson's Disease Patients.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 14;15(4):1243. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041243. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LW, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF (2015) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14, 625–639. - PubMed
-
- Knudsen K, Fedorova TD, Hansen AK, Sommerauer M, Haase AM, Svendsen KB, Otto M, Ostergaard K, Krogh K, Borghammer P (2019) Objective intestinal function in patients with idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 58, 28–34. - PubMed
-
- Goetze O, Nikodem AB, Wiezcorek J, Banasch M, Przuntek H, Mueller T, Schmidt WE, Woitalla D (2006) Predictors of gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 18, 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Goetze O, Wieczorek J, Mueller T, Przuntek H, Schmidt WE, Woitalla D (2005) Impaired gastric emptying of a solid test meal in patients with Parkinson’s disease using 13C-sodium octanoate breath test. Neurosci Lett 375, 170–173. - PubMed
-
- Hardoff R, Sula M, Tamir A, Soil A, Front A, Badarna S, Honigman S, Giladi N (2001) Gastric emptying time and gastric motility in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16, 1041–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

