Neuroprotective Effects of Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats by Calcium Channel Mediating Hydrogen Sulfide
- PMID: 32804313
- PMCID: PMC11443989
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-020-00940-0
Neuroprotective Effects of Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats by Calcium Channel Mediating Hydrogen Sulfide
Abstract
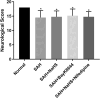
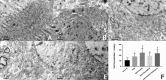
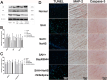
The present study explored the modulating apoptosis effect of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) rats and its exact mechanism. A rat SAH model established by intravascular puncturing was used for the present study. After giving NaHS (donor of H2S), an L-type calcium channel opener (Bay K8644), or a calcium channel agonist (nifedipine), the neurological function of the rats, associated pathological changes, and expression of apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3) and microtubule-associated protein (MAP-2) were examined. The concentration of H2S and expression of cystathionine beta synthase in the hippocampus changed upon early brain injury (EBI) after SAH. Compared with the SAH group, the neurological function of the rats and microstructure observed by electron microscopy were better in the SAH + NaHS group and SAH + Bay K8644 group. It was observed that apoptosis was more obvious in the SAH group than in the control group and was alleviated in the SAH + NaHS group. Furthermore, the alleviating effect of NaHS was partially weakened by nifedipine, indicating that the effect of anti-apoptosis in H2S might be correlated with the calcium channel. The expression of Bax and caspase-3 was elevated, while the expression of Bcl-2 decreased in the SAH group but improved in the SAH + NaHS and SAH + Bay K8644 group. Compared with the SAH + NaHS group, the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins was higher in the SAH + NaHS + nifedipine group. Therefore, upon EBI following SAH, the H2S system plays an important neurological protective effect by modulating the function of the L-type calcium channel and inhibiting apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Calcium channel; Early brain injury; Hydrogen sulfide; Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
© 2020. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Ameliorates Early Brain Injury Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;53(6):3646-3657. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9304-1. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26111628
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide Against Early Brain Injury and Secondary Cognitive Deficits Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Brain Pathol. 2017 Jan;27(1):51-63. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12361. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 26822402 Free PMC article.
-
H2S induces vasoconstriction of rat cerebral arteries via cAMP/adenylyl cyclase pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;289(3):389-96. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.021. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26524654
-
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates brain edema in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: Possible involvement of MMP-9 induced blood-brain barrier disruption and AQP4 expression.Neurosci Lett. 2016 May 16;621:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.018. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 27080433
-
GLP-1R Agonist Liraglutide Attenuates Inflammatory Reaction and Neuronal Apoptosis and Reduces Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Inflammation. 2021 Feb;44(1):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01344-4. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 32951103
Cited by
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Localization and Expression of p53 and Cell Death in the Nervous Tissue in Traumatic Brain Injury and Axotomy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 28;24(21):15708. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115708. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958692 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide to repair cardiovascular injury after trauma.Nitric Oxide. 2022 Dec 1;129:82-101. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Nitric Oxide. 2022. PMID: 36280191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Regulation of Cell Death following Neurotrauma and Related Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10742. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310742. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):15-25. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01166-4. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35066714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Incidence and Mechanisms.Stroke. 2023 May;54(5):1426-1440. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.040072. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Stroke. 2023. PMID: 36866673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Mufti F, Amuluru K, Smith B, Damodara N, El-Ghanem M, Singh IP, Dangayach N, Gandhi CD (2017) Emerging markers of early brain injury and delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg 107:148–159 - PubMed
-
- Avanzato D, Merlino A, Porrera S, Wang R, Munaron L, Mancardi D (2014) Role of calcium channels in the protective effect of hydrogen sulfide in rat cardiomyoblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem 33(4):1205–1214 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

