Omipalisib Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth Through Inactivation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) and ERK Signaling
- PMID: 32804918
- PMCID: PMC7450785
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.927106
Omipalisib Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth Through Inactivation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) and ERK Signaling
Abstract
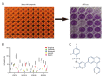
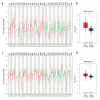
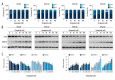
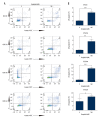
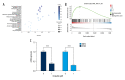
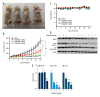
BACKGROUND Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a life-threatening digestive tract malignancy with no known curative treatment. This study aimed to investigate the antineoplastic effects of omipalisib and its underlying molecular mechanisms in ESCC using a high throughput screen. MATERIAL AND METHODS MTT assay and clone formation were used to determine cell viability and proliferation. Flow cytometry was conducted to detect cell cycle distribution and apoptosis. Global gene expression and mRNA expression levels were determined by RNA sequencing and real-time PCR, respectively. Protein expression was evaluated in the 4 ESCC cell lines by Western blot analysis. Finally, a xenograft nude mouse model was used to evaluate the effect of omipalisib on tumor growth in vivo. RESULTS In the pilot screening of a 1404-compound library, we demonstrated that omipalisib markedly inhibited cell proliferation in a panel of ESCC cell lines. Mechanistically, omipalisib induced G₀/G₁ cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. RNA-seq, KEGG, and GSEA analyses revealed that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is the prominent target of omipalisib in ESCC cells. Treatment with omipalisib decreased expression of p-AKT, p-4EBP1, p-p70S6K, p-S6, and p-ERK, therefore disrupting the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK signaling. In the nude mouse xenograft model, omipalisib significantly suppressed the tumor growth in ESCC tumor-bearing mice without obvious adverse effects. CONCLUSIONS Omipalisib inhibited the proliferation and growth of ESCC by disrupting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK signaling. The present study supports the rationale for using omipalisib as a therapeutic approach in ESCC patients. Further clinical studies are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SOX2 promotes tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling pathway.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jul;104(7):810-6. doi: 10.1111/cas.12155. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23510069 Free PMC article.
-
SLC39A14 promotes the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jan 27;146:113831. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113831. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39700956
-
Methylation of NRN1 is a novel synthetic lethal marker of PI3K-Akt-mTOR and ATR inhibitors in esophageal cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Jul;112(7):2870-2883. doi: 10.1111/cas.14917. Epub 2021 May 16. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33931924 Free PMC article.
-
A Pleiotropic Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Modulation of Wnt/β-Catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implication in Chemotherapeutic Drug Response.Curr Oncol. 2022 Mar 26;29(4):2326-2349. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29040189. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35448163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review: PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Its Regulated Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factors May Be a Potential Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 28;12:817916. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.817916. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35574327 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs With Efficacy in Preclinical In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2022 May-Jun;19(3):283-298. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20320. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35430563 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Cancer Strategy Based on Changes in the Role of Autophagy Depending on the Survival Environment and Tumorigenesis Stages.Molecules. 2024 Oct 30;29(21):5134. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215134. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arntl-induced upregulation of DUSP1 inhibits tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inactivating ERK signaling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2408042. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2408042. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39341782 Free PMC article.
-
Three generations of mTOR kinase inhibitors in the activation of the apoptosis process in melanoma cells.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):975-989. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00748-9. Epub 2023 Apr 25. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37097377 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Axis: Potential for Sarcoma Therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(16):1496-1520. doi: 10.2174/0113895575270904231129062137. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38265369 Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global incidence of esophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64(3):381–87. - PubMed
-
- Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Esophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):400–12. - PubMed
-
- Murray JC, Levy B. Repurposed drugs trials by cancer type: Lung cancer. Cancer J. 2019;25(2):127–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

