Efficacy of Yoga vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs Stress Education for the Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32805013
- PMCID: PMC7788465
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
Efficacy of Yoga vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs Stress Education for the Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is common, impairing, and undertreated. Although many patients with GAD seek complementary and alternative interventions, including yoga, data supporting yoga's efficacy or how it compares to first-line treatments are lacking.
Objectives: To assess whether yoga (Kundalini yoga) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for GAD are each more effective than a control condition (stress education) and whether yoga is noninferior to CBT for the treatment of GAD.
Design, setting, and participants: For this randomized, 3-arm, controlled, single-blind (masked independent raters) clinical trial, participants were recruited from 2 specialty academic centers starting December 1, 2013, with assessment ending October 25, 2019. Primary analyses, completed by February 12, 2020, included superiority testing of Kundalini yoga and CBT vs stress education and noninferiority testing of Kundalini yoga vs CBT.
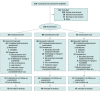
Interventions: Participants were randomized to Kundalini yoga (n = 93), CBT for GAD (n = 90), or stress education (n = 43), which were each delivered to groups of 4 to 6 participants by 2 instructors during twelve 120-minute sessions with 20 minutes of daily homework.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary intention-to-treat outcome was acute GAD response (Clinical Global Impression-Improvement Scale score of much or very much improved) after 12 weeks as assessed by trained independent raters.
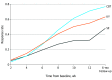
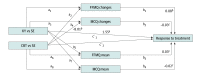
Results: Of 538 participants who provided consent and were evaluated, 226 (mean [SD] age, 33.4 [13.5] years; 158 [69.9%] female) with a primary diagnosis of GAD were included in the trial. A total of 155 participants (68.6%) completed the posttreatment assessment. Completion rates did not differ (Kundalini yoga, 60 [64.5%]; CBT, 67 [74.4%]; and stress education, 28 [65.1%]: χ2 = 2.39, df = 2, P = .30). Response rates were higher in the Kundalini yoga group (54.2%) than in the stress education group (33.%) (odds ratio [OR], 2.46 [95% CI, 1.12-5.42]; P = .03; number needed to treat, 4.59 [95% CI, 2.52-46.19]) and in the CBT group (70.8%) compared with the stress education group (33.0%) (OR, 5.00 [95% CI, 2.12-11.82]; P < .001; number needed to treat, 2.62 [95% CI, 1.91-5.68]). However, the noninferiority test did not find Kundalini yoga to be as effective as CBT (difference, 16.6%; P = .42 for noninferiority).
Conclusions and relevance: In this trial, Kundalini yoga was efficacious for GAD, but the results support CBT remaining first-line treatment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01912287.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of preference for yoga or cognitive behavioral therapy in patients with generalized anxiety disorder on treatment outcomes and engagement.J Psychiatr Res. 2022 Sep;153:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Psychiatr Res. 2022. PMID: 35810600 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Yoga for generalized anxiety disorder: design of a randomized controlled clinical trial.Contemp Clin Trials. 2015 Sep;44:70-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Contemp Clin Trials. 2015. PMID: 26255236 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Efficacy of Electronically Delivered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (e-CBT) to Weekly Online Mental Health Check-Ins for Generalized Anxiety Disorder-A Randomized Controlled Trial: Comparaison de l'efficacité de la thérapie cognitivo-comportementale délivrée par voie électronique (e-TCC) aux contrôles hebdomadaires en ligne de santé mentale pour le trouble d'anxiété généralisée - un essai randomisé contrôlé.Can J Psychiatry. 2024 Sep;69(9):695-707. doi: 10.1177/07067437241261933. Epub 2024 Jul 21. Can J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39033431 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.Depress Anxiety. 2018 Jun;35(6):502-514. doi: 10.1002/da.22728. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Depress Anxiety. 2018. PMID: 29451967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing Cognitive Behavioral Therapy versus Yoga for Helping Older Adults Address High Levels of Worry [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Mar. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Mar. PMID: 38237006 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Digital Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs Medication Therapy Among Patients With Insomnia.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Apr 3;6(4):e237597. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.7597. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37040111 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of intermittent fasting on physical activity: a national survey of Chinese residents aged 18-80 years.Front Physiol. 2025 May 12;16:1582036. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1582036. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40421454 Free PMC article.
-
Selected Trends in Psychotherapy Research: An Index Analysis of RCTs.Clin Psychol Eur. 2022 Jun 30;4(2):e7921. doi: 10.32872/cpe.7921. eCollection 2022 Jun. Clin Psychol Eur. 2022. PMID: 36397942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of yin yoga intervention on state and trait anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 14;15:1345455. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1345455. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38550540 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of risk factors affecting knee injury during yoga based on medical big data analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 22;104(34):e43926. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043926. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40859498 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

