Allopurinol-Induced Oral Lichenoid Drug Reaction with Complete Regression after Drug Withdrawal
- PMID: 32806618
- PMCID: PMC7583598
- DOI: 10.3390/dermatopathology7020004
Allopurinol-Induced Oral Lichenoid Drug Reaction with Complete Regression after Drug Withdrawal
Abstract
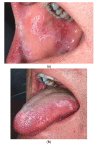
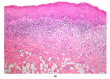
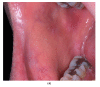
Background: Lichen planus is a chronic mucocutaneous inflammatory disease. Oral manifestations are common, and may remain exclusive to the oral mucosa without involvement of the skin or other mucosae. A differential diagnosis includes oral lichenoid drug reactions. Allopurinol, which is the first line hypo-uricemic treatment, is often quoted as being a possible offending drug, though oral reactions have rarely been reported. Case presentation: We describe a 59-year-old male gout patient, successfully treated with allopurinol, who developed acute onset of oral lichenoid lesions, involving bilaterally the buccal mucosa, the tongue and the labial mucosa. Histopathology was consistent with a lichen planus or a drug-induced lichenoid reaction. Improvement of the patient's condition after withdrawal of allopurinol confirmed the lichenoid nature of the lesion. Remission was complete after a few weeks. Discussion: Although unusual, allopurinol may induce a lichenoid drug reaction. These reactions may mimic clinically and histopathologically idiopathic lichen planus. Improvement or complete regression of the lesions may be attempted to confirm the diagnosis. According to the latest WHO recommendations, these lesions have a potential for malignant transformation.
Keywords: adverse drug reaction; allopurinol; lichen planus; lichenoid reaction; oral mucosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Carbamazepine-Induced Oral Lichenoid Reaction: A Report of a Rare Case.Cureus. 2025 Apr 7;17(4):e81835. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81835. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40337574 Free PMC article.
-
Histomorphometric analysis of nuclear and cellular volumetric alterations in oral lichen planus, lichenoid lesions and normal oral mucosa using image analysis software.Indian J Dent Res. 2013 Mar-Apr;24(2):277. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.116678. Indian J Dent Res. 2013. PMID: 23965463
-
Allopurinol-amplified lichenoid reactions of the oral mucosa.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984 Oct;58(4):397-400. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(84)90331-1. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984. PMID: 6593665
-
Oral lichen planus: A disease or a spectrum of tissue reactions? Types, causes, diagnostic algorhythms, prognosis, management strategies.Periodontol 2000. 2019 Jun;80(1):105-125. doi: 10.1111/prd.12260. Periodontol 2000. 2019. PMID: 31090143 Review.
-
Lichen planus and lichenoid reactions of the oral mucosa.Dermatol Ther. 2010 May-Jun;23(3):251-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01322.x. Dermatol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20597944 Review.
References
-
- Saurat J.-H., Lipsker D., Thomas L., Borradori L., Lachapelle J.-M. Dermatologie Et Infections Sexuellement Transmissibles. 6th ed. Elsevier-Masson; Paris, France: 2017.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

