Genomic Insight of VIM-harboring IncA Plasmid from a Clinical ST69 Escherichia coli Strain in Italy
- PMID: 32806766
- PMCID: PMC7466171
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8081232
Genomic Insight of VIM-harboring IncA Plasmid from a Clinical ST69 Escherichia coli Strain in Italy
Abstract
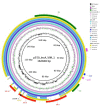
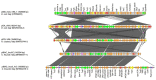
Background: VIM (Verona Integron-encoded Metallo-beta-lactamase) is a member of the Metallo-Beta-Lactamases (MBLs), and is able to hydrolyze all beta-lactams antibiotics, except for monobactams, and including carbapenems. Here we characterize a VIM-producing IncA plasmid isolated from a clinical ST69 Escherichia coli strain from an Italian Long-Term Care Facility (LTCF) inpatient. Methods: An antimicrobial susceptibility test and conjugation assay were carried out, and the transferability of the blaVIM-type gene was confirmed in the transconjugant. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of the strain 550 was performed using the Sequel I platform. Genome assembly was performed using "Microbial Assembly". Genomic analysis was conducted by uploading the contigs to ResFinder and PlasmidFinder databases. Results: Assembly resulted in three complete circular contigs: the chromosome (4,962,700 bp), an IncA plasmid (p550_IncA_VIM_1; 162,608 bp), harboring genes coding for aminoglycoside resistance (aac(6')-Ib4, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(3')-XV, aph(6)-Id), beta-lactam resistance (blaSHV-12, blaVIM-1), macrolides resistance (mph(A)), phenicol resistance (catB2), quinolones resistance (qnrS1), sulphonamide resistance (sul1, sul2), and trimethoprim resistance (dfrA14), and an IncK/Z plasmid (p550_IncB_O_K_Z; 100,306 bp), free of antibiotic resistance genes. Conclusions: The increase in reports of IncA plasmids bearing different antimicrobial resistance genes highlights the overall important role of IncA plasmids in disseminating carbapenemase genes, with a preference for the blaVIM-1 gene in Italy.
Keywords: E. coli; IncA; blaVIM-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Lauretti L., Riccio M.L., Mazzariol A., Cornaglia G., Amicosante G., Fontana R., Rossolini G.M. Cloning and characterization of blaVIM, a new integron-borne metallo-beta-lactamase gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999;43:1584–1590. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.7.1584. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

