Phase II Study of Immunotherapy With Tecemotide and Bevacizumab After Chemoradiation in Patients With Unresectable Stage III Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NS-NSCLC): A Trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E6508)
- PMID: 32807654
- PMCID: PMC7606595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.06.007
Phase II Study of Immunotherapy With Tecemotide and Bevacizumab After Chemoradiation in Patients With Unresectable Stage III Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NS-NSCLC): A Trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E6508)
Abstract
Introduction: Although chemoradiotherapy (CRT) is the standard of care for patients with unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (LA-NSCLC), most patients relapse. Tecemotide is a MUC1 antigen-specific cancer immunotherapy vaccine. Bevacizumab improves survival in advanced nonsquamous (NS)-NSCLC and has a role in immune modulation. This phase II trial tested the combination of tecemotide and bevacizumab following CRT in patients with LA-NSCLC.
Patients and methods: Subjects with stage III NS-NSCLC suitable for CRT received carboplatin/paclitaxel weekly + 66 Gy followed by 2 cycles of consolidation carboplatin/paclitaxel ≤ 4 weeks of completion of CRT (Step 1). Patients with partial response/stable disease after consolidation therapy were registered onto step 2, which was 6 weekly tecemotide injections followed by every 6 weekly injections and bevacizumab every 3 weeks for up to 34 doses. The primary endpoint was to determine the safety of this regimen.
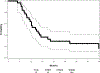
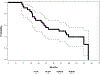
Results: Seventy patients were enrolled; 68 patients (median age, 63 years; 56% male; 57% stage IIIA) initiated therapy, but only 39 patients completed CRT and consolidation therapy per protocol, primarily owing to disease progression or toxicity. Thirty-three patients (median age, 61 years; 58% male; 61% stage IIIA) were registered to step 2 (tecemotide + bevacizumab). The median number of step 2 cycles received was 11 (range, 2-25). Step 2 worst toxicity included grade 3, N = 9; grade 4, N = 1; and grade 5, N = 1. Grade 5 toxicity in step 2 was esophageal perforation attributed to bevacizumab. Among the treated and eligible patients (n = 32) who were treated on step 2, the median overall survival was 42.7 months (95% confidence interval, 21.7-63.3 months), and the median progression-free survival was 14.9 months (95% confidence interval, 11.0-20.9 months) from step 1 registration.
Conclusions: This cooperative group trial met its endpoint, demonstrating tolerability of bevacizumab + tecemotide after CRT and consolidation. In this selected group of patients, the median progression-free survival and overall survival are encouraging. Given that consolidation immunotherapy is now a standard of care following CRT in patients with LA-NSCLC, these results support a role for continued investigation of antiangiogenic and immunotherapy combinations in LA-NSCLC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Locally advanced NSCLC; Radiation; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Auperin A, Le Pechoux C, Pignon JP, Koning C, Jeremic B, Clamon G, et al. Concomitant radio-chemotherapy based on platin compounds in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a meta-analysis of individual data from 1764 patients. Ann Oncol 2006;17(3):473–83 doi 10.1093/annonc/mdj117. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le Chevalier T, Arriagada R, Quoix E, Ruffie P, Martin M, Douillard JY, et al. Radiotherapy alone versus combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy in unresectable non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 1994;10 Suppl 1:S239–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UG1 CA189873/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 CA182843/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189830/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233327/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180870/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA201543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233331/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233247/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous