Years of Life Lost Attributable to COVID-19 in High-incidence Countries
- PMID: 32808515
- PMCID: PMC7431288
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e300
Years of Life Lost Attributable to COVID-19 in High-incidence Countries
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is a major public health problem of international concern. It is important to estimate its impact of COVID-19 for health policy decision-making. We estimated the years of life lost (YLLs) due to COVID-19 in high-incidence countries.
Methods: We collected the YLLs due to COVID-19 in 30 high-incidence countries as of April 13, 2020 and followed up as of July 14, 2020. Incidence and mortality were collected using each country's formal reports, articles, and other electronic sources. The life expectancy of Japanese females by age and the UN population data were used to calculate YLLs in total and per 100,000.
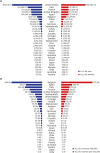
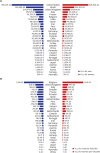
Results: As of April 22, 2020, there were 1,699,574 YLLs due to COVID-19 in 30 high-incidence countries. On July 14, 2020, this increased to 4,072,325. Both on April 22 and July 14, the total YLLs due to COVID-19 was highest in the USA (April 22, 534,481 YLLs; July 14, 1,199,510 YLLs), and the YLLs per 100,000 population was highest in Belgium (April 22, 868.12 YLLs/100,000; July 14, 1,593.72 YLLs/100,000). YLLs due to COVID-19 were higher among males than among females and higher in those aged ≥ 60 years than in younger individuals. Belgium had the highest proportion of YLLs attributable to COVID-19 as a proportion of the total YLLs and the highest disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 population.
Conclusion: This study estimated YLLs due to COVID-19 in 30 countries. COVID-19 is a high burden in the USA and Belgium, among males and the elderly. The YLLs are very closely related with the incidence as well as the mortality. This highlights the importance of the early detection of incident case that minimizes severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 fatality.
Keywords: Burden of Disease; COVID-19; Disability-Adjusted Life Years; SARS-CoV-2; Years of Life Lost.
© 2020 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Burden of Disease due to COVID-19 in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Jun 1;35(21):e199. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e199. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32476305 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19, Australia: Epidemiology Report 16 (Reporting week to 23:59 AEST 17 May 2020).Commun Dis Intell (2018). 2020 May 22;44. doi: 10.33321/cdi.2020.44.45. Commun Dis Intell (2018). 2020. PMID: 32522141
-
COVID-19, Australia: Epidemiology Report 18 (Fortnightly reporting period ending 7 June 2020).Commun Dis Intell (2018). 2020 Jun 17;44. doi: 10.33321/cdi.2020.44.52. Commun Dis Intell (2018). 2020. PMID: 32552623
-
Diagnostic and methodological evaluation of studies on the urinary shedding of SARS-CoV-2, compared to stool and serum: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020 Sep 30;66(6):148-156. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020. PMID: 33040802
-
Predicted COVID-19 fatality rates based on age, sex, comorbidities and health system capacity.BMJ Glob Health. 2020 Sep;5(9):e003094. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003094. BMJ Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32912856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estimation of Excess Mortality and Years of Life Lost to COVID-19 in Norway and Sweden between March and November 2020.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 8;18(8):3913. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18083913. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33917872 Free PMC article.
-
Is Mandatory Vaccination in Population over 60 Adequate to Control the COVID-19 Pandemic in E.U.?Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Feb 18;10(2):329. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020329. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214788 Free PMC article.
-
Years of life lost (YLL) associated with COVID-19 deaths in Khorasan-RAZAVI province, Iran.J Public Health (Oxf). 2023 Mar 14;45(1):259-266. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdab392. J Public Health (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 34927698 Free PMC article.
-
Male-Female Disparities in Years of Potential Life Lost Attributable to COVID-19 in the United States: A State-by-State Analysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 5:2021.05.02.21256495. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.02.21256495. medRxiv. 2021. PMID: 33972951 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) due to the direct health impact of COVID-19 in India, 2020.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 14;12(1):2454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06505-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35165362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it. [Updated 2020]. [Accessed April 28, 2020]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica....
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 – 11 March 2020. [Updated 2020]. [Accessed April 27, 2020]. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. [Updated 2020]. [Accessed April 28, 2020]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

