Kidney transplant program waitlisting rate as a metric to assess transplant access
- PMID: 32808730
- PMCID: PMC7980228
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16277
Kidney transplant program waitlisting rate as a metric to assess transplant access
Abstract
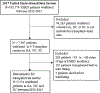
Kidney transplant program performance in the United States is commonly measured by posttransplant outcomes. Inclusion of pretransplant measures could provide a more comprehensive assessment of transplant program performance and necessary information for patient decision-making. In this study, we propose a new metric, the waitlisting rate, defined as the ratio of patients who are waitlisted in a center relative to the person-years referred for evaluation to a program. Furthermore, we standardize the waitlisting rate relative to the state average in Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina. The new metric was used as a proof-of-concept to assess transplant-program access compared to the existing transplant rate metric. The study cohorts were defined by linking 2017 United States Renal Data System (USRDS) data with transplant-program referral data from the Southeastern United States between January 1, 2012 and December 31, 2016. Waitlisting rate varied across the 9 Southeastern transplant programs, ranging from 10 to 22 events per 100 patient-years, whereas the program-specific waitlisting rate ratio ranged between 0.76 and 1.33. Program-specific waitlisting rate ratio was uncorrelated with the transplant rate ratio (r = -.15, 95% CI, -0.83 to 0.57). Findings warrant collection of national data on early transplant steps, such as referral, for a more comprehensive assessment of transplant program performance and pretransplant access.
Keywords: Scientific Registry for Transplant Recipients (SRTR); ethics and public policy; health services and outcomes research; kidney disease; kidney transplantation/nephrology; patient referral; quality of care/care delivery; registry/registry analysis.
© 2020 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures



Comment in
-
Shifting transplant center performance evaluations upstream.Am J Transplant. 2021 Jan;21(1):7-8. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16335. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 33037722 No abstract available.
-
Renal Transplantation and Renovascular Hypertension.J Urol. 2021 Aug;206(2):465-466. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001852. Epub 2021 May 12. J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33975454 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chandraker A, Andreoni KA, Gaston RS, et al. Time for reform in transplant program-specific reporting: AST/ASTS transplant metrics taskforce. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(7):1888–1895. - PubMed
-
- Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients. Program-specific reports. 2019. https://www.srtr.org/. Accessed May 20, 2019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

