Assessment of shoulder rotation strength, muscle co-activation and shoulder pain in tetraplegic wheelchair athletes - A methodological study
- PMID: 32808885
- PMCID: PMC9135435
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2020.1803659
Assessment of shoulder rotation strength, muscle co-activation and shoulder pain in tetraplegic wheelchair athletes - A methodological study
Abstract
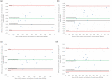
Objective: To develop a feasible protocol for testing maximum shoulder rotation strength in tetraplegic wheelchair athletes, and investigate concurrent validity of maximum isometric handheld dynamometer (HHD) towards maximum isokinetic dynamometer (ID) strength measurements; secondly, to study shoulder muscle activation during maximum shoulder rotation measurements, and the association between shoulder strength and shoulder pain.Design: Descriptive methodological.Setting: Danish Wheelchair Rugby (WCR) association for WCR tetraplegic athletes from local WCR-clubs.Participants: Twelve adult tetraplegics.Interventions: N/A.Outcome measures: Wheelchair User's Shoulder Pain Index (WUSPI) and Visual Analog Scale (VAS) measured shoulder pain, isometric HHD and ID (60°/s) measured maximum internal (IR) and external (ER) shoulder rotation strength. Surface Electromyography normalized to maximum EMG measured muscle activity (mm Infraspinatus and Latissimus Dorsi) during maximum shoulder rotation strength.Results: Concurrent validity of isometric HHD towards ID showed Concordance Correlation Coefficients of left and right arms 0.90 and 0.86 (IR), and 0.89 and 0.91 (ER), with no difference in muscle activity between isometric HHD and ID, but larger co-activation during ER. There was no association between shoulder strength and pain, except for significantly weak negative associations between ID and pain during ER for left and right arms (P = 0.03; P = 0.04).Conclusion: Standardized feasible protocol for tetraplegic wheelchair athletes for measuring maximum shoulder rotation strength was established. Isometric HHD is comparable with ID on normalized peak torques and muscle activity, but with larger co-activation. Strength was not clearly associated with shoulder pain.
Keywords: Electromyography; Feasible protocol; Isokinetic dynamometer; Isometric handheld dynamometer; WUSPI.
Figures


References
-
- Ballinger DA, Rintala DH, Hart KA.. The relation of shoulder pain and range-of-motion problems to functional limitations, disability, and perceived health of men with spinal cord injury: a multifaceted longitudinal study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000;81(12):1575–81. doi: 10.1053/apmr.2000.18216 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luime JJ, Koes BW, Hendriksen IJ, et al. . Prevalence and incidence of shoulder pain in the general population; a systematic review. ScandJRheumatol 2004;33(2):73–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
