A newly discovered role of metabolic enzyme PCK1 as a protein kinase to promote cancer lipogenesis
- PMID: 32809272
- PMCID: PMC7494067
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12084
A newly discovered role of metabolic enzyme PCK1 as a protein kinase to promote cancer lipogenesis
Abstract
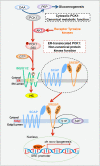
Highly active lipogenesis is essential for rapid tumor growth. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) is a key transcriptional factor for lipogenesis and activated by reduced sterol and oxysterol levels. However, the mechanism by which cancer cells activate SREBP without altering these sterol/oxysterol levels remains elusive. In one of our recent studies published in Nature entitled "The gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 phosphorylates INSIG1/2 for lipogenesis", we demonstrated that activated AKT-mediated phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (PCK1) S90 phosphorylation reduces the gluconeogenic activity of PCK1 and triggers its translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where PCK1 acts as a protein kinase and uses GTP, rather than ATP, as a phosphate donor to phosphorylate Insig1/2 thereby reducing oxysterol's binding to Insig1/2 and activating SREBP-mediated lipogenesis for tumor growth. These findings elucidate a coordinated regulation between gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and uncover a critical role of the protein kinase activity of PCK1 in SREBP-dependent lipid synthesis.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases