Ozone: a natural bioactive molecule with antioxidant property as potential new strategy in aging and in neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 32810649
- PMCID: PMC7428719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101138
Ozone: a natural bioactive molecule with antioxidant property as potential new strategy in aging and in neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
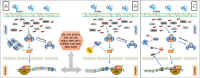
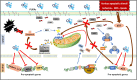
Systems medicine is founded on a mechanism-based approach and identifies in this way specific therapeutic targets. This approach has been applied for the transcription factor nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). Nrf2 plays a central role in different pathologies including neurodegenerative disorders (NDs), which are characterized by common pathogenetic features. We here present wide scientific background indicating how a natural bioactive molecule with antioxidant/anti-apoptotic and pro-autophagy properties such as the ozone (O3) can represent a potential new strategy to delay neurodegeneration. Our hypothesis is based on different evidence demonstrating the interaction between O3 and Nrf2 system. Through a meta-analytic approach, we found a significant modulation of O3 on endogenous antioxidant-Nrf2 (p < 0.00001, Odd Ratio (OR) = 1.71 95%CI:1.17-2.25) and vitagene-Nrf2 systems (p < 0.00001, OR = 1.80 95%CI:1.05-2.55). O3 activates also immune, anti-inflammatory signalling, proteasome, releases growth factors, improves blood circulation, and has antimicrobial activity, with potential effects on gut microbiota. Thus, we provide a consistent rationale to implement future clinical studies to apply the oxygen-ozone (O2-O3) therapy in an early phase of aging decline, when it is still possible to intervene before to potentially develop a more severe neurodegenerative pathology. We suggest that O3 along with other antioxidants (polyphenols, mushrooms) implicated in the same Nrf2-mechanisms, can show neurogenic potential, providing evidence as new preventive strategies in aging and in NDs.
Keywords: Neurodegenerative Disorders; Oxygen-Ozone (O(2)-O(3)) therapy; Ozone (O(3)); antioxidant system; nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)–like 2 (Nrf2); stress oxidative biomarkers.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed L.A., Salem H.A., Mawsouf Mohamed N, Attia Amina S, Agha A.M. Cardioprotective effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning in an in vivo model of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation. 2012;(72):345–354. JID - 0404375. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S.M., Luo L., Namani A., Wang X.J., Tang X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017;1863:585–597. - PubMed
-
- Ajamieh H., Merino N., Candelario-Jalil E., Menendez S., Martinez-Sanchez G., Re L., Giuliani A., Leon O.S. Similar protective effect of ischaemic and ozone oxidative preconditionings in liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol. Res. 2002;45:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Ajamieh H.H., Berlanga J., Merino N., Sanchez G.M., Carmona A.M., Cepero S.M., Giuliani A., Re L., Leon O.S. Role of protein synthesis in the protection conferred by ozone-oxidative-preconditioning in hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion. Transpl. Int. 2005;18:604–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

