The development of Coronavirus 3C-Like protease (3CLpro) inhibitors from 2010 to 2020
- PMID: 32810751
- PMCID: PMC7409838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112711
The development of Coronavirus 3C-Like protease (3CLpro) inhibitors from 2010 to 2020
Abstract
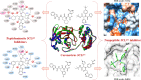
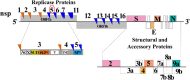
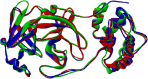
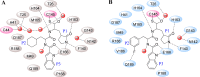
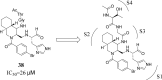
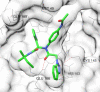
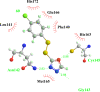
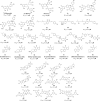
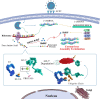
This review fully describes the coronavirus 3CLpro peptidomimetic inhibitors and nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors developed from 2010 to 2020. Specifically, the structural characteristics, binding modes and SARs of these 3CLpro inhibitors are expounded in detail by division into two categories: peptidomimetic inhibitors mainly utilize electrophilic warhead groups to covalently bind the 3CLpro Cys145 residue and thereby achieve irreversible inhibition effects, whereas nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors mainly interact with residues in the S1', S1, S2 and S4 pockets via hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic bonds and van der Waals forces. Based on the emerging PROTAC technology and the existing 3CLpro inhibitors, 3CLpro PROTAC degraders are hypothesised to be next-generation anti-coronavirus drugs.
Keywords: 3C-like protease (3CL(pro)) inhibitors; COVID-19; Coronaviruses; Peptidomimetic inhibitors; Proteolytic targeting chimaera (PROTAC).
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








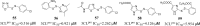



References
-
- Hui D.S., E I.A., Madani T.A., Ntoumi F., Kock R., Dar O., Ippolito G., McHugh T.D., Memish Z.A., Drosten C., Zumla A., Petersen E. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health - the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. : IJID : Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2020;91:264–266. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J.F., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C., Poon R.W., Tsoi H.W., Lo S.K., Chan K.H., Poon V.K., Chan W.M., Ip J.D., Cai J.P., Cheng V.C., Chen H., Hui C.K., Yuen K.Y. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet (London, England) 2020;395:514–523. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

