Association of PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32811452
- PMCID: PMC7433068
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-020-01098-8
Association of PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide. Current studies have shown that PNPLA3 (Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3) rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism is associated with adult nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [1, 2].But there is no consensus on the relationship between PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism and children NAFLD due to differences in population samples. To this end, a meta-analysis of published research is conducted to comprehensively assess the relationship between PNPLA3 gene polymorphism and NAFLD in children.
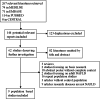
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases from inception to May 2019. Case-control studies assessing the relationship between PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children were selected according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. Random effects model was used to quantify the association between the PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism and the susceptibility of children's NAFLD. Fixed effects model was used to quantify the relationship between the PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism and the severity of NAFLD in children. The Stata 12.0 software was employed for data analysis.
Results: A total of nine case-control studies were included in this meta-analysis containing data of 1173 children with NAFLD and 1792 healthy controls. Five studies compared NAFLD children and non-NAFLD healthy populations. Statistical analysis showed that PNPLA3 gene polymorphism was significantly associated with children's NAFLD in the allele contrast, dominant, recessive and over dominant models (G vs C,OR = 3.343, 95% CI = 1.524-7.334; GG + GC vs CC,OR = 3.157, 95% CI = 1.446-6.892;GG vs GC + CC,OR = 5.692, 95% CI = 1.941-16.689; GG + CC vs GC,OR = 2.756, 95% CI = 1.729-4.392). Four case-control studies compared Children with nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and children with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The results showed that the PNPLA3 gene polymorphism was also significantly associated with the severity of NAFLD in children in recessive gene model (GG vs GC + CC,OR = 14.43, 95% CI = 5.985-34.997); The Egger's test revealed no significant publication bias.
Conclusions: Meta-analysis showed that PNPLA3 gene polymorphism was significantly associated with susceptibility and severity of NAFLD in children.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; PNPLA3; Polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) susceptibility and severity: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(7):e14324. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014324. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30762732 Free PMC article.
-
Association between rs738409 polymorphism in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) gene and hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: Evidence from case-control studies.Gene. 2019 Feb 15;685:143-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 4. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30403964 Review.
-
Association of single nucleotide polymorphism at PNPLA3 with fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and cirrhosis of liver.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep;36(5):366-372. doi: 10.1007/s12664-017-0784-y. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28975533
-
Association of PNPLA3 rs738409 C > G and rs2896019 T > G Polymorphisms with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Turkish Population from Adıyaman Province.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2025 Mar;29(3):63-73. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2024.0481. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2025. PMID: 40101239
-
Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2011 Jun;53(6):1883-94. doi: 10.1002/hep.24283. Epub 2011 May 14. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21381068
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the ability of insulin resistance and lipid-related indices to predict the presence of NAFLD in obese adolescents.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 2;23(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02144-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38956572 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children.Pediatr Obes. 2021 Nov;16(11):e12849. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12849. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Pediatr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34498413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the role of genetic variations in NAFLD: implications for disease pathogenesis and precision medicine approaches.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 20;29(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01708-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38504356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Increasing Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents Worldwide and in Mexico and the Implications for Public Health.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Aug 30;27:e934134. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934134. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 34456329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease from childhood to adulthood: State of art and future directions.World J Hepatol. 2022 Jun 27;14(6):1087-1098. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1087. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35978659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mazo DF, Malta FM, Stefano JT, et al. Validation of PNPLA3 polymorphisms as risk factor for NAFLD and liver fibrosis in an admixed population. Ann Hepatol. 2019;18(3):466-71. - PubMed
-
- Sood V, Khanna R, Rawat D, et al. Predictive risk factors and transient elastography in pediatric non alcoholic fatty liver disease in Indian population. J Pediatr Gastr Nutr. 2018;66:84. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001641. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

