Targeting EphA2 in cancer
- PMID: 32811512
- PMCID: PMC7433191
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00944-9
Targeting EphA2 in cancer
Abstract
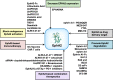
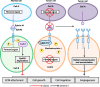
Eph receptors and the corresponding Eph receptor-interacting (ephrin) ligands jointly constitute a critical cell signaling network that has multiple functions. The tyrosine kinase EphA2, which belongs to the family of Eph receptors, is highly produced in tumor tissues, while found at relatively low levels in most normal adult tissues, indicating its potential application in cancer treatment. After 30 years of investigation, a large amount of data regarding EphA2 functions have been compiled. Meanwhile, several compounds targeting EphA2 have been evaluated and tested in clinical studies, albeit with limited clinical success. The present review briefly describes the contribution of EphA2-ephrin A1 signaling axis to carcinogenesis. In addition, the roles of EphA2 in resistance to molecular-targeted agents were examined. In particular, we focused on EphA2's potential as a target for cancer treatment to provide insights into the application of EphA2 targeting in anticancer strategies. Overall, EphA2 represents a potential target for treating malignant tumors.
Keywords: Cancer; EphA2 receptor; Ephrin A1; Target; Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ireton RC, Chen J. EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005;5(3):149–157. - PubMed
-
- Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987;238(4834):1717–1720. - PubMed
-
- Dodelet VC, Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2000;19(49):5614–5619. - PubMed
-
- Heroult M, Schaffner F, Augustin HG. Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):642–650. - PubMed
-
- Kullander K, Klein R. Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(7):475–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

