De novo assembly and characterization of the liver transcriptome of Mugil incilis (lisa) using next generation sequencing
- PMID: 32811897
- PMCID: PMC7435268
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70902-5
De novo assembly and characterization of the liver transcriptome of Mugil incilis (lisa) using next generation sequencing
Abstract
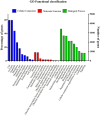
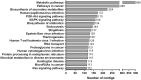
Mugil incilis (lisa) is an important commercial fish species in many countries, living along the coasts of the western Atlantic Ocean. It has been used as a model organism for environmental monitoring and ecotoxicological investigations. Nevertheless, available genomic and transcriptomic information for this organism is extremely deficient. The aim of this study was to characterize M. incilis hepatic transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing. A total of 32,082,124 RNA-Seq read pairs were generated utilizing the HiSeq platform and subsequently cleaned and assembled into 93,912 contigs (N50 = 2,019 bp). The analysis of species distribution revealed that M. incilis contigs had the highest number of hits to Stegastes partitus (13.4%). Using a sequence similarity search against the public databases GO and KEGG, a total of 7,301 and 16,967 contigs were annotated, respectively. KEGG database showed genes related to environmental information, metabolism and organismal system pathways were highly annotated. Complete or partial coding DNA sequences for several candidate genes associated with stress responses/detoxification of xenobiotics, as well as housekeeping genes, were employed to design primers that were successfully tested and validated by RT-qPCR. This study presents the first transcriptome resources for Mugil incilis and provides basic information for the development of genomic tools, such as the identification of RNA markers, useful to analyze environmental impacts on this fish Caribbean species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A survey of the complex transcriptome from the highly polyploid sugarcane genome using full-length isoform sequencing and de novo assembly from short read sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2017 May 22;18(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3757-8. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28532419 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq analysis of Quercus pubescens Leaves: de novo transcriptome assembly, annotation and functional markers development.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112487. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393112 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly and characterization of bark transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.).BMC Genomics. 2012 May 18;13:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-192. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22607098 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of starch and sucrose metabolism across bulb development in Sagittaria sagittifolia.Gene. 2018 Apr 5;649:99-112. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.075. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29374598 Review.
-
At the dawn of the transcriptomic medicine.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Feb;246(3):286-292. doi: 10.1177/1535370220954788. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 32915637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822) from polluted and non-polluted rivers in India.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 10;20(4):e0320358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320358. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40209169 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Pollution and Advances in Biomonitoring in Cartagena Bay in the Colombian Caribbean.Toxics. 2023 Jul 20;11(7):631. doi: 10.3390/toxics11070631. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37505596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

