Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer's disease brain
- PMID: 32812023
- PMCID: PMC7526722
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awaa223
Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer's disease brain
Abstract
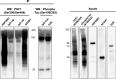
Accumulation of phosphorylated tau is a key pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease. Phosphorylated tau accumulation causes synaptic impairment, neuronal dysfunction and formation of neurofibrillary tangles. The pathological actions of phosphorylated tau are mediated by surrounding neuronal proteins; however, a comprehensive understanding of the proteins that phosphorylated tau interacts with in Alzheimer's disease is surprisingly limited. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the phosphorylated tau interactome. To this end, we used two complementary proteomics approaches: (i) quantitative proteomics was performed on neurofibrillary tangles microdissected from patients with advanced Alzheimer's disease; and (ii) affinity purification-mass spectrometry was used to identify which of these proteins specifically bound to phosphorylated tau. We identified 542 proteins in neurofibrillary tangles. This included the abundant detection of many proteins known to be present in neurofibrillary tangles such as tau, ubiquitin, neurofilament proteins and apolipoprotein E. Affinity purification-mass spectrometry confirmed that 75 proteins present in neurofibrillary tangles interacted with PHF1-immunoreactive phosphorylated tau. Twenty-nine of these proteins have been previously associated with phosphorylated tau, therefore validating our proteomic approach. More importantly, 34 proteins had previously been associated with total tau, but not yet linked directly to phosphorylated tau (e.g. synaptic protein VAMP2, vacuolar-ATPase subunit ATP6V0D1); therefore, we provide new evidence that they directly interact with phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer's disease. In addition, we also identified 12 novel proteins, not previously known to be physiologically or pathologically associated with tau (e.g. RNA binding protein HNRNPA1). Network analysis showed that the phosphorylated tau interactome was enriched in proteins involved in the protein ubiquitination pathway and phagosome maturation. Importantly, we were able to pinpoint specific proteins that phosphorylated tau interacts with in these pathways for the first time, therefore providing novel potential pathogenic mechanisms that can be explored in future studies. Combined, our results reveal new potential drug targets for the treatment of tauopathies and provide insight into how phosphorylated tau mediates its toxicity in Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; neurofibrillary tangles; phosphorylation; proteomics; tau.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Augustinack JC, Sanders JL, Tsai LH, Hyman BT. Colocalization and fluorescence resonance energy transfer between cdk5 and AT8 suggests a close association in pre-neurofibrillary tangles and neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002; 61: 557–64. - PubMed
-
- Babu JR Geetha T Wooten MW. Sequestosome 1/p62 shuttles polyubiquitinated tau for proteasomal degradation. J Neurochem 2005; 94: 192–203. - PubMed
-
- Baumann K, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Piwnica-Worms H, Mandelkow E. Abnormal Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau-protein by cyclin-dependent kinases cdk2 and cdk5. FEBS Lett 1993; 336: 417–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

