Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the lung: A report of seven cases
- PMID: 32812677
- PMCID: PMC7529556
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13614
Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the lung: A report of seven cases
Abstract
Signet-ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) is an extremely rare subtype of adenocarcinoma with aggressive behavior that usually occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, prostate or breast. In this study, we described the clinicopathological and prognostic characteristics of, and the therapeutic strategies for seven patients with primary SRCC of the lung from Sichuan University West China Hospital to enhance our understanding of this kind of tumor. According to the information presented herein, it is believed that patients with primary pulmonary SRCC can live for a long time if the cancer is diagnosed early and treated actively. However, more investigations are still needed due to the limited reports about primary SRCC of the lung. KEY POINTS: SIGNIFICANT FINDINGS OF THE STUDY: Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the lung is an extremely rare subtype of lung adenocarcinoma and is relatively highly invasive. WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS: Early diagnosis and positive treatment lead to a good prognosis for patients with signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Case report; lung; signet-ring cell carcinoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
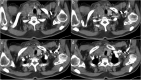
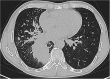
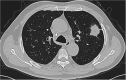
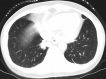
References
-
- Kish JK, Ro JY, Ayala AG, McMurtrey MJ. Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung with signet‐ring cells: A histochemical comparison with signet‐ring cell carcinomas of the other sites. Hum Pathol 1989; 20: 1097–102. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y, Brambilla E. World Health Organization: International Histological Classification of Tumors: Histological Typing of Lung and Pleural Tumors. Springer, Heidelberg: 1999.
-
- Castro CY, Moran CA, Flieder DG, Suster S. Primary signet ring cell adenocarcinomas of the lung: A clinicopathological study of 15 cases. Histopathology 2001; 39 (4): 397–401. - PubMed
-
- Ou SH, Ziogas A, Zell JA. Primary signet‐ring carcinoma (SRC) of the lung: A population‐based epidemiologic study of 262 cases with comparison to adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol 2010; 5 (4): 420–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

