How to Handle Concomitant Asymptomatic Prosthetic Joints During an Episode of Hematogenous Periprosthetic Joint Infection, a Multicenter Analysis
- PMID: 32813012
- PMCID: PMC9187975
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1222
How to Handle Concomitant Asymptomatic Prosthetic Joints During an Episode of Hematogenous Periprosthetic Joint Infection, a Multicenter Analysis
Abstract
Background: Prosthetic joints are at risk of becoming infected during an episode of bacteremia, especially during Staphylocococcus aureus bacteremia. However, it is unclear how often asymptomatic periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) occurs, and whether additional diagnostics should be considered.
Methods: In this multicenter study, we retrospectively analyzed a cohort of patients with a late acute (hematogenous) PJI between 2005-2015 who had concomitant prosthetic joints in situ. Patients without at least 1 year of follow-up were excluded.
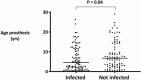
Results: We included 91 patients with a hematogenous PJI and 108 concomitant prosthetic joints. The incident PJI was most frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus (43%), followed by streptococci (26%) and Gram-negative rods (18%). Of 108 concomitant prosthetic joints, 13 were symptomatic, of which 10 were subsequently diagnosed as a second PJI. Of the 95 asymptomatic prosthetic joints, 1 PJI developed during the follow-up period and was classified as a "missed" PJI at the time of bacteremia with S. aureus (1.1%). Infected prosthetic joints were younger than the noninfected ones in 67% of cases, and prosthetic knees were affected more often than prosthetic hips (78%).
Conclusions: During an episode of hematogenous PJI, concomitant asymptomatic prosthetic joints have a very low risk of being infected, and additional diagnostic work-up for these joints is not necessary.
Keywords: asymptomatic; bacteremia; hematogenous; late acute; periprosthetic joint infection.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Vail TP, Berry DJ. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009; 91:128–33. - PubMed
-
- Saleh A, Guirguis A, Klika AK, Johnson L, Higuera CA, Barsoum WK. Unexpected positive intraoperative cultures in aseptic revision arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2014; 29:2181–6. - PubMed
-
- Zeller V, Kerroumi Y, Meyssonnier V, et al. Analysis of postoperative and hematogenous prosthetic joint-infection microbiological patterns in a large cohort. J Infect 2018; 76:328–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical