IRGM links autoimmunity to autophagy
- PMID: 32813580
- PMCID: PMC8007158
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1810920
IRGM links autoimmunity to autophagy
Abstract
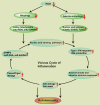
IRGM is a genetic risk factor for several autoimmune diseases. However, the mechanism of IRGM-mediated protection in autoimmunity remains undetermined. The abnormal activation of type I interferon (IFN) response is one of the significant factors in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases. In our recent study, we showed that IRGM is a master suppressor of the interferon response. We found that the depletion of IRGM results in constitutively activated CGAS-STING1, DDX58/RIG-I-MAVS, and TLR3-TICAM1/TRIF signaling pathways resulting in upregulation of almost all IFN-responsive genes. Mechanistically, IRGM utilizes a two-pronged mechanism to suppress the interferon response. First, it mediates SQSTM1/p62-dependent selective macroautophagy/autophagy of nucleic acid sensor proteins, including CGAS, DDX58/RIG-I, and TLR3. Second, it facilitates the removal of defective mitochondria by mitophagy and avoids a buildup of mito-ROS and mito-damage/danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Thus, IRGM deficiency results in increased nucleic acid sensors and DAMPs engaging a vicious cycle of aberrant activation of IFN response that is known to occur in systemic autoimmune-like conditions.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; DAMPs; IRGM; IRGM1; RIG-I-MAVS; autophagy; cGAS-STING; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
