Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates
- PMID: 32813950
- PMCID: PMC9632334
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916525
Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates
Abstract
Background: Bisphosphonates are effective in reducing hip and osteoporotic fractures. However, concerns about atypical femur fractures have contributed to substantially decreased bisphosphonate use, and the incidence of hip fractures may be increasing. Important uncertainties remain regarding the association between atypical femur fractures and bisphosphonates and other risk factors.
Methods: We studied women 50 years of age or older who were receiving bisphosphonates and who were enrolled in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California health care system; women were followed from January 1, 2007, to November 30, 2017. The primary outcome was atypical femur fracture. Data on risk factors, including bisphosphonate use, were obtained from electronic health records. Fractures were radiographically adjudicated. Multivariable Cox models were used. The risk-benefit profile was modeled for 1 to 10 years of bisphosphonate use to compare associated atypical fractures with other fractures prevented.
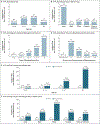
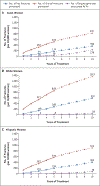
Results: Among 196,129 women, 277 atypical femur fractures occurred. After multivariable adjustment, the risk of atypical fracture increased with longer duration of bisphosphonate use: the hazard ratio as compared with less than 3 months increased from 8.86 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.79 to 28.20) for 3 years to less than 5 years to 43.51 (95% CI, 13.70 to 138.15) for 8 years or more. Other risk factors included race (hazard ratio for Asians vs. Whites, 4.84; 95% CI, 3.57 to 6.56), height, weight, and glucocorticoid use. Bisphosphonate discontinuation was associated with a rapid decrease in the risk of atypical fracture. Decreases in the risk of osteoporotic and hip fractures during 1 to 10 years of bisphosphonate use far outweighed the increased risk of atypical fracture among Whites but less so among Asians. After 3 years, 149 hip fractures were prevented and 2 bisphosphonate-associated atypical fractures occurred in Whites, as compared with 91 and 8, respectively, in Asians.
Conclusions: The risk of atypical femur fracture increased with longer duration of bisphosphonate use and rapidly decreased after bisphosphonate discontinuation. Asians had a higher risk than Whites. The absolute risk of atypical femur fracture remained very low as compared with reductions in the risk of hip and other fractures with bisphosphonate treatment. (Funded by Kaiser Permanente and others.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 26;383(22):2188. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2029828. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33252880 No abstract available.
-
Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 26;383(22):2188-2189. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2029828. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33252881 No abstract available.
-
Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 26;383(22):2189. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2029828. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33252882 No abstract available.
-
Atypical Femur Fracture Risk versus Fragility Fracture Prevention with Bisphosphonates. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 26;383(22):2189-2190. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2029828. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33252883 No abstract available.
-
In women, bisphosphonate use for ≥3 years vs. <3 months was linked to increased atypical femur fracture risk.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Jan;174(1):JC9. doi: 10.7326/ACPJ202101190-009. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33395342
References
-
- Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005–2025. J Bone Miner Res 2007; 22: 46575. - PubMed
-
- Khosla S, Bilezikian JP, Dempster DW, et al. Benefits and risks of bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012; 97:2 272–82. - PubMed
-
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Lancet 1996; 348: 1535–41. - PubMed
-
- Eastell R, Rosen CJ, Black DM, Cheung AM, Murad MH, Shoback D. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019; 104: 1595–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
